Very High Frequency (VHF)
From Signal Identification Wiki
(Redirected from VHF)
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) encompasses frequencies from 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz to 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'Vario' Airplane Data Controller | This transmitter is found within the UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) FMRS bands, most likely used at airshows to give off barometric pressure, height in altitude represented by a voice, including various tones representing how high/how low the model plane is in the air. | 462.61 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 462.725 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 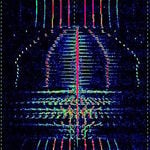 |
||
| 17067bps FSK | Unknown military-use signal reminiscent of SECURENET CVSD voice. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 88 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 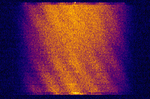 |
|
| 49MHz RC Car Controller | The sound of an RC controller signal from an old amphibious toy car | 49.2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 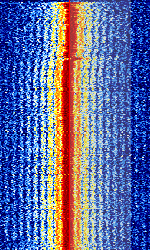 |
||||
| 77Ya6 'Voronezh' radar | Voronezh (Воронеж) is a Russian radar family capable of aircraft and ballistic missile monitoring. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 440 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | FMCW | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Russia |  |
|
| AFSK Paging Link | A variant of POCSAG/FLEX with audio FSKFrequency-Shift Keying modulation based off of the bell 202 tones. Typically found as uplinks/downlinks to pager network transmitters. | 72 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 928 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying | 9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 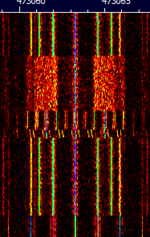 |
|
| ALE-400 | ALEAutomatic Link Establishment-400 is an amateur version of the 2G ALEAutomatic Link Establishment standard. It is adapted to the demands of amateur radio emergency traffic handling. | 1.806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.163 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 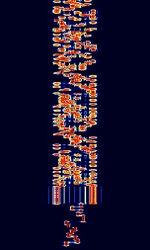 |
|
| AMSAT-P3D | AMSAT-P3D (Known as Phase 3D, OSCAR-40, and AO-40) is a amateur radio satellite built by AMSAT. As of 2004, the satellite's systems have failed. | 145.805 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 24,048.285 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 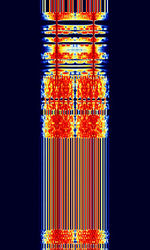 |
|
| ATSC Broadcast | Advanced Television Systems Committee Television. 8VSB Modulation | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | 8VSB | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | United States | — |  |
| Aircraft Communications Addressing and Reporting System (ACARS) | ACARS is a digital datalink system for the transmission of short messages between aircraft and ground stations via airband radio or satellite. | 129 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 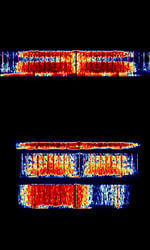 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation (AM) | Long range commercial broadcast and international radio. Also used for aviation communications. | 153 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 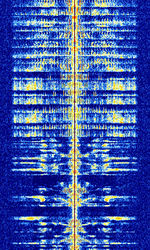 |
|
| Autocab | This is an example of the Autocab Media Data Terminals used by cab companies all over the world. | 163.375 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United Kingdom | 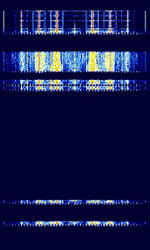 |
|
| Automatic Identification System (AIS) | Automatic Identification System (AIS) is used by ships to broadcast position and vessel information. | 161.975 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 162.025 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 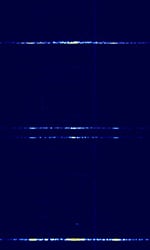 |
|
| Automatic Packet Reporting System (APRS) | Packet system for real time data communications. Used by hams for location reporting, weather stations etc. | 144.39 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 432.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 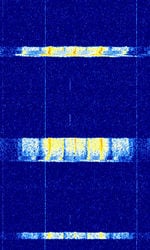 |
|
| Automatic Picture Transmission (APT) | Automatic Picture Transmission (APT), also known as NOAA-GEOSAT, was an analog image transmission mode used by the NOAA weather satellites and some Russian weather satellites to transmit satellite weather photos. As of august 2025, most of the NOAA sats that transmitted this mode have been decommissioned, and have discontinued transmission. | 137.1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 137.913 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 34 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 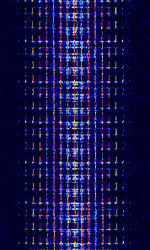 |
|
| Automatic Transmitter Identification System (ATIS) | ATIS systems are identification tags used by inland commercial waterway traffic on rivers in Europe. The FSKFrequency-Shift Keying burst is appended at the end of every voice transmission by the vessel operator. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 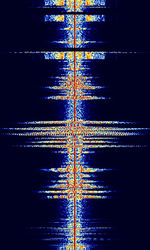 |
|
| B-Netz | B-Netz, was an analog, commercial mobile radio telephone network that was operated by the Deutsche Bundespost in Germany (at first only West Germany) from 1972 until 1994. The system was also implemented in neighboring countries Austria, The Netherlands and Luxembourg. | 148 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 153 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 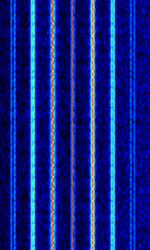 |
|
| Binary Interchange of Information and Signaling (BIIS) | BIIS (also known as BIIS 1200) is an ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards. protocol for a digital selective calling method with the added benefit of extended capability of transmitting data that exceeds what could be done with old 5-tone analog calling methods like CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) and ZVEI. | 35 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 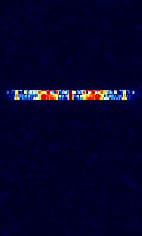 |
|
| CAS-4A/B Satellite Telemetry | CAS-4A/B Satellite 4.8 kbpsKilobits per second (kbps) GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying Telemetry Downlink. | 145.835 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 145.89 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 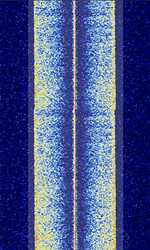 |
|
| CCIR Selcall | CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) selcall consists of CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R)-1, CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R)-2, and PCCIR, which are 5-tone selcall modes for VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz)/UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) radios. CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R)-1 and CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R)-2 only differ in the tone duration, and PCCIR only differs in the group, reset, and repeat tone frequencies. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 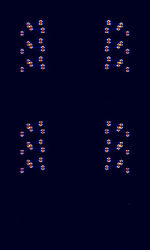 |
|
| CCITT | CCITT is a 5-tone selcall system for VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz)/UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) radios. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| CODAR | CODAR (Coastal Ocean Dynamics Applications Radar) is used for near-surface ocean monitoring, such as waves and water current. | 4.438 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 42.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | ILFM | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 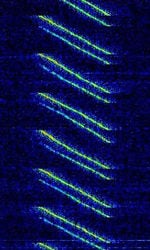 |
|
| CRY2001 Voice Scrambler | CRY2001 is a voice scrambling mode used on Sailor CRY2001 Scramblers. Fisherman often use these modes to communicate with privacy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 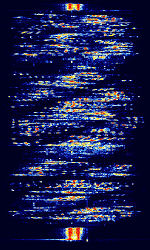 |
|
| Canadian Meteor Orbit Radar (CMOR) | Canadian Meteor Orbit Radar, or CMOR, is a meteor detection radar located near Tavistock, Ontario. | 17.45 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 38.15 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | Pulsed | 28 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Canada | 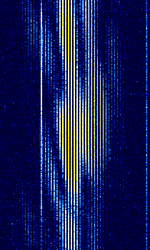 |
|
| Chilean Naval Time Signal | Naval VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) time signal found in Chilean Coast, in Vina Del Mar | 148.125 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Chile | 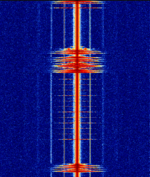 |
|
| China digital radio (CDR) | Convergent Digital Radio (CDR) or China Digital Radio is an in-band-on-channel (IBOCIn-Band On-Channel (IBOC) is a hybrid method of transmitting digital radio and analog radio broadcast signals simultaneously on the same frequency.) digital radio broadcasting format used in China. It can be found in multiple bandwidth configurations with different modulation formats. | 106.1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 500 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 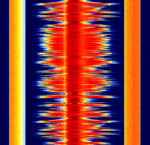 |
|
| Chinese/Asian radio "MDC1200" | Many Asian borne handheld transceivers will have the menu option for a roger beep and many of them like baofengs and radtels will have a option for a roger beep called "TONE1200" and this is to mimic the sounds you would hear on analog police networks. But the thing is most radios fail to do that and it sounds more like a MPT1327 packet. | 136 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 16 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | WORLDWIDE | 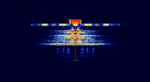 |
|
| Continuous Tone-Coded Squelch System (CTCSS) | CTCSS, also known as Private Line and Channel Guard, is a low continuous tone transmitted on NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation voice transmissions that is used to squelch and manage transmissions on a given frequency. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | CWContinuous Wave | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 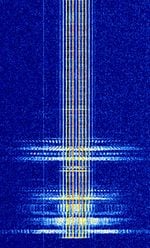 |
|
| D-STAR | D-STAR is a digital voice protocol used by ham radio. Is sometimes routed over the internet for international communications. | 145.67 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 6.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 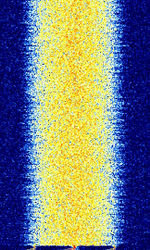 |
|
| Datawell Buoy HF Link | Datawell Buoy HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Links transmitted by Datawell Marine measurement buoys, measuring ocean conditions, temperature, and wave current. | 25.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 45 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 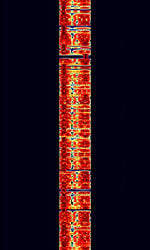 |
|
| Delfi-C3 Telemetry | Delfi-C3 Telemetry was a telemetry signal sent from the Delfi-C3 university-class satellite. | 145.87 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | LSBLower Side Band Modulation | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 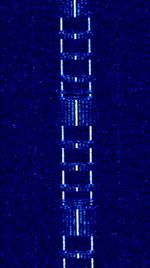 |
|
| Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) | DAB is an audio broadcasting standard containing a multiplex of digital radio stations in the signal. | 174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 239 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.536 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | ||
| Digital Audio Broadcasting Plus (DAB+) | DAB+ is a medium of delivering broadcast radio, containing multiple stations in a single multiplex. | 174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 230 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.536 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | |||
| Digital Dispatch Systems MDT | Digital Dispatch Systems Mobile Data Terminal is a dispatching system used by taxi and private transportation companies. | 152 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 854.788 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States |  |
|
| Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) | Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) is an open digital mobile radio standard defined by ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards. and used in commercial products around the world. Mostly used by private network and local police, can be encrypted. Used in MOTOTRBO products. | 66 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 860 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 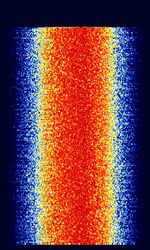 |
|
| Digital Multimedia Broadcasting (DMB) | Digital Multimedia Broadcasting (DMB) is a digital radio transmission technology developed in South Korea as part of the national IT project for sending multimedia such as TV, radio and datacasting to mobile devices such as mobile phones, laptops and GPS navigation systems. | 174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 216 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | DQPSKDifferential Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.536 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | South Korea | — |  |
|
| Digital NBTV | Method for transmitting digital images via radio, similar to WinDRM or KG-STV | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Digital Private Mobile Radio (dPMR) | dPMR is an open, non-proprietary trunked radio standard developed by ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards., published under ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards. TS 102 658. Supports both data and digital voice transmission. | 149.019 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 446.2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 6.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 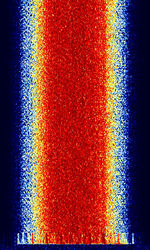 |
|
| Digital Radio Mondiale Plus (DRM+) | DRM+ is a VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) implementation of DRM primarily for the FMFrequency Modulation broadcast band. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 230 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
|
| Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial (DVB-T) | Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial (DVB-T) is a digital broadcast television format used in Europe and in many other countries in the world. | 174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 786 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Distress Radiobeacon (Analog) | Analog Distress Radiobeacons are simple siren-based transmitters that were installed in older EPIRB's, PLB's and ELT's. Currently used as a supplementary homing signal in modern digital radiobeacons. | 121.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 243 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | ||
| Dual Tone Multi Frequency (DTMF) | DTMF is a signaling mode used for a variety of purposes. It's most known for telephony dialing, but is in use for many different applications such as DTMF paging for DTMF-enabled VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz)/UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) radios. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 3.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| EEA | EEA is a 5-tone selcall mode defined by the Electronic Engineering Association in the United Kingdom. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| EIA | EIA is a 5/6-tone selcall mode defined by the Electronics Industries Association in the United States. Also known as Motorola MetroPage. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| EURO | EURO is a 6/7-tone selcall mode used in VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz)/UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) radios. Also known as EuroSignal. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Emergency Alert System (EAS) | The Emergency Alert System (EAS) is a national warning system in the United States, implemented since 1997, superceding the Emergency Broadcast System (EBS). | 162.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 162.55 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying | 1.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 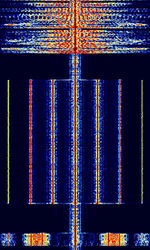 |
|
| Emergency Managers Weather Information Network (EMWIN) - Repeater | The Emergency Managers Weather Information Network (EMWIN) is a system for distributing a live stream of weather information in the United States. This is the VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) Repeater of the network. | 163.3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 168.813 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 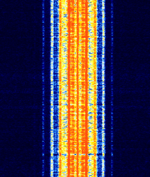 |
|
| Enhanced Digital Access Communications System (EDACS) | EDACS is a trunked radio system developed by General Electric and Ericsson. EDACS was invented by General Electric in the mid-80s and is currently owned by Harris Corporation. Harris has announced that EDACS systems will no longer be supported by 2017. | 160 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 6.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 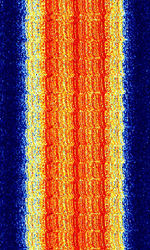 |
|
| European Radio Message System (ERMES) | European Radio Message System (ERMES) is a European common standard for paging developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ESTI) | 169.413 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 169.833 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 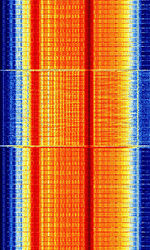 |
|
| FLEX | FLEX (Flexible Wide Area Paging Protocol) is Motorola's high speed one-way paging protocol that supports 1600, 3200, and 6400 bpsBits per second (bps). FLEX can transmit tone, numeric, alphanumeric, and binary data. | 152.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 931.938 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 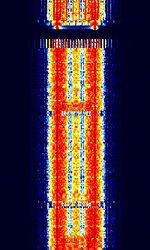 |
|
| FM Broadcast Radio | Commercial Broadcast FMFrequency Modulation radio stations. Used for the broadcast of many different radio programs, including music, news, sports, weather, and talk shows. | 65 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 38 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 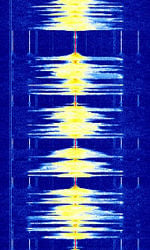 |
|
| FM NBTV | FMFrequency Modulation NBTV is a method to send moving images in a very narrow bandwidth (maximum 3 KHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz) | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 2.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 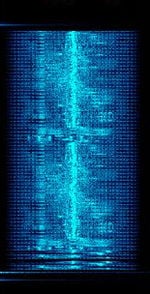 |
|
| FSK441 | FSK441 is a high speed meteor scatter communication mode. FSK441 uses a baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. rate of 441 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 144 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 444 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 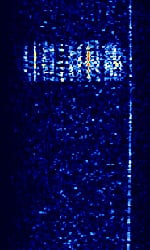 |
|
| FT4 | FT4 is an amateur radio contesting communication protocol developed by Joe Taylor (K1JT) and Steve Franke (K9AN) descended from FT8. | 10.14 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 144.17 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 83 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 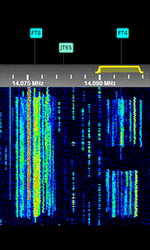 |
|
| FT8 | FT8 is an extremely-weak-signal amateur radio mode that transmits very limited communications. JS8, a variant of FT8, can send full conversations and relay messages | 1.84 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 8-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 50 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 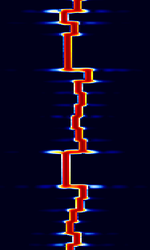 |
|
| FUNcube-1 Telemetry | FUNcube-1 Telemetry is a telemetry signal sent from the Funcube-1 Cubesat amateur radio satellite. | 145.935 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 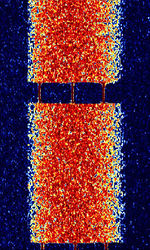 |
|
| Federal Signal Modem-MSK | Signalling protocol developed for Federal Signal's various warning and mass notification appliances. This signal is used for activation and telemetry of all units in a network. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 160 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 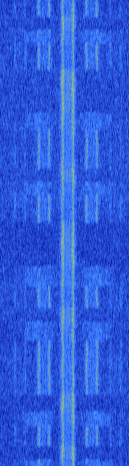 |
|
| Futuba RC Controller | 72-75 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz transmitters are used to control various types of RC models. RC Controllers that use 72-75 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz don't seem to be used as often as they used to. | 72 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 75 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 12 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 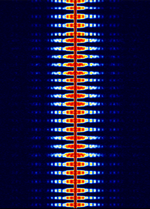 |
|||
| GMDSS Digital Selective Calling | Global Maritime Distress and Safety System's Digital Selective Calling (GMDSS-DSC) is a maritime communication protocol intended to initiate ship-to-ship, ship-to-shore and shore-to-ship radiotelephone and MFMedium Frequency (300-3000 kHz)/HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) radiotelex calls. | 2.177 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 156.525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 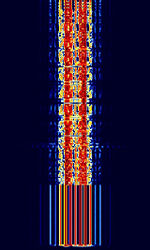 |
|
| GRAVES | The Grand Réseau Adapté à la Veille Spatiale (GRAVES) system is a French space-surveillance system for low-orbit (up to 1000km) satellites. Emitter is based near Dijon, France. | 143.05 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW I/Q | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | France | 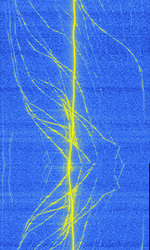 |
||
| Gandalf MDT | Gandalf MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office. was developed by Gandalf Mobile Systems, a subsidiary of Canadian company Gandalf Technologies. Used primarily by taxi and courier services in Canada and the United States. This protocol was used in Gandalf's Cabmate systems. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 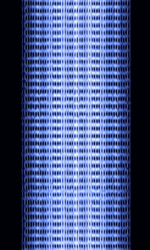 |
|
| Glenayre Paging Link | Glenayre's Paging Link. With QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation being used, It is a way to upkeep a linked paging transmitter when no data is broadcast. Glenayre C2100/C2000 model control systems were likely to use this. | 152 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 512 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | United States | 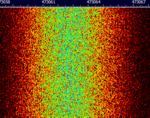 |
||
| Golay Paging (GSC) | Golay Paging (or Golay Sequential Code, GSC) is a one-way 2-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying paging format developed by Motorola. It is capable of transmitting tone, numeric, alphanumeric, and voice pages. | 33 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 932 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 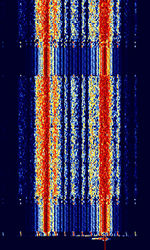 |
|
| Gonets | Gonets (Russian Гонец, for Messenger) is a Russian civilian low Earth orbit communications satellite system. | 265 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 388 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 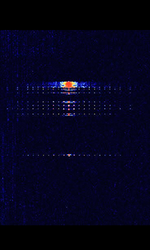 |
|
| Ground-Based Augmentation System (GBAS) | GBAS is an advanced aircraft navigation system that provides GPS corrections to aircraft on approach. | 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 117.975 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | D8PSK | 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 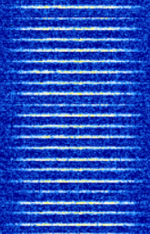 |
|
| HC-265 Voice Scrambler | HC-265 is a Voice Scrambling mode developed by Hagelin Crypto for their HC-265 CRYPTOCOM secure voice unit. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 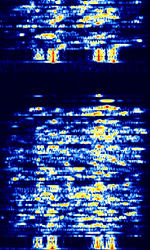 |
|
| HD Radio (FM) | HD Radio is a proprietary digital broadcast radio format transmitted in North America, usually as sidebands on analog carriers. This is the FMFrequency Modulation band implementation of HD Radio. | 87.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 107.9 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 400 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 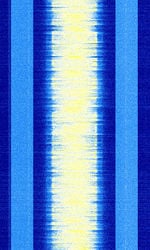 |
|
| HDMI RFI Clock | HDMI is a popular media source for delivering video, audio, all in the same stream. Unfortunately, there is massive interference from it when a neighboring SDR is near it. It can disrupt receiving to a great degree. | 148.35 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 742.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 700 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | — | 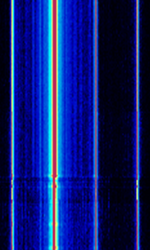 |
|
| ICAO Selcal | ICAO Selcal (also known as AVCALL, ANNEX 10, or just SELCAL) is a HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz)/VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) aviation selective calling system used by ground stations to initiate radio communications with aircraft. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 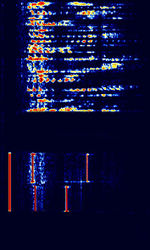 |
|
| ILS Marker Beacon | ILS Marker Beacons are used by aircraft for Instrument Landing Systems, transmitted by an upward-facing directive antenna at known distances along the approach path. | 75 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 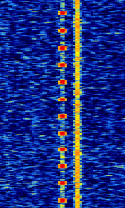 |
|
| ISCAT | Ionospheric Scattering (ISCAT) mode used for weak signal long distance radio contact by meteor and Ionosphere scattering. | 50 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 148 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 904 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.809 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 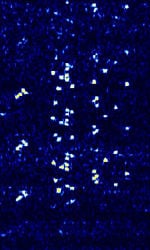 |
|
| Instrument Landing System | Radio navigation system that allows aircraft to perform precision approaches in low visibility conditions. | 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 335 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
||
| Interoperable Electronic Train Management System (I-ETMS) | Transmits train telemetry | 219 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 222 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | US | 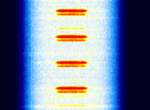 |
|
| Ionized Meteor Trails | Meteors traversing the E region of the atmosphere approximately 60 - 90 miles up create ionizing trails which can reflect and refract radio waves from commercial FMFrequency Modulation radio stations that are hundreds and sometimes thousands of miles away from the receiver. | 88.3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | CWContinuous Wave | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 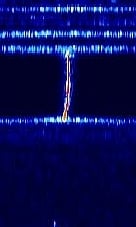 |
|
| JS8 | JS8Call is an extremely-weak-signal amateur radio communication mode based on FT8. It allows FT8 to be used for conversations and message relaying. | 1.842 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 50.318 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 50 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 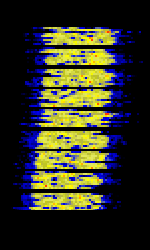 |
|
| JT4 | JT4 is a 4-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying extreme weak-signal mode which is designed especially for Earth-Moon-Earth communications. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 17 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 949 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
||
| JT65 | JT65 is an amateur radio QSO communication protocol developed by Joe Taylor, K1JT. JT65 has 3 submodes: JT65A, JT65B, and JT65C. The most popular submode of JT65 is JT65A. JT65 gets '65' from the 65 tones it uses. | 1.838 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 50.276 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 180 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 710 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 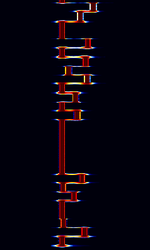 |
|
| JT6M | JT6M is part of the WSJT suite of digital weak signal software applications developed by Joe Taylor, K1JT | 50.215 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 50.25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 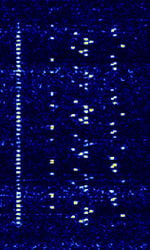 |
|
| JT9 | JT9 is a 9-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode for making contact (QSO's) under extreme weak-signal conditions. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | 3.578 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.079 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 16 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.78 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 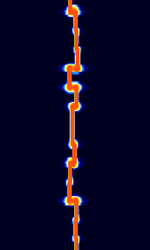 |
|
| Kenwood FleetSync | FleetSync is a manufacturer specific signaling standard which includes a number of features: unit ID, status, emergency button, inhibit, status check, GPS, and selective calling. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 850 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | — | 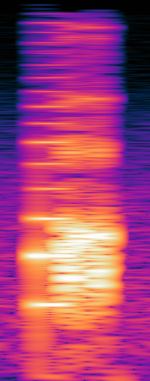 |
|
| Kiwi | Kiwi is a telemetry mode developed by CNES used on amateur rockets and radio balloons in France. | 137.95 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 138.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | France | 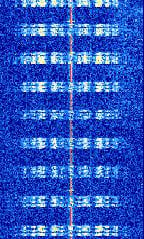 |
|
| LoJack | LoJack is a vehicle tracking system that allows vehicles to be tracked by police, with the aim of recovering them in case of theft via a small radio transceiver clandestinely installed in a vehicle. | 173.075 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Logic Trunked Radio (LTR) | Logic Trunked Radio, is an analog trunked radio format developed by EF Johnson Company. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 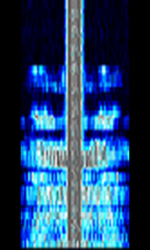 |
||
| MDC1200 | MDC (Motorola Data Communications), also known as Stat-Alert, MDC-1200 and MDC-600, is a Motorola two-way radio low-speed data system. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 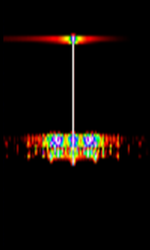 |
|
| MMP-4800 | MMP-4800 was a MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office. (Mobile Data Terminal) protocol developed by Canadian company Mobile Data International (MDI) in 1982 for their Mobile Data Terminals. Used by public safety and commercial industries. Phased out. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 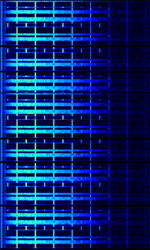 |
||
| MODAT | MODAT is a 7-tone Automatic Number Identification (ANI) status system used by handheld radios. It provides unit ID and emergency statuses to receiving radio sets when transmitted. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| MPT 1327 | MPT1327 (Ministry of Posts and Telegraph 1327) is a signaling protocol standard for analog trunked radio | 162.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying, FMFrequency Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 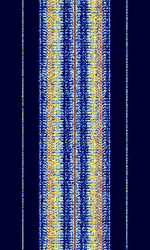 |
|
| MSK144 | MSK144 is a Minimum Shift Keying FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signal used for amateur radio meteor-scatter contacts. It transmits 144 bit long packets at a baudrate of 2000 bpsBits per second (bps) using frequencies 1000 and 2000 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 440 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 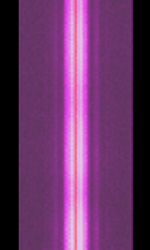 |
|
| Monaco Enterprises MAAP Fire Alarm | Fire alarm control panel built for the United States of America's Department of Defense. | 138.95 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 139.675 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States |  |
|
| Morse Code (CW) | CWContinuous Wave Morse Code is the simplest form of transmission found virtually all over the RFRadio Frequency bands for a variety of uses. The most common use of this is for Call-sign Beacons by both Amateur and Military operators. | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 250,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | Worldwide |  |
||
| Motorola SECURENET | Motorola SECURENET ("analog" encryption) was a secure voice option for conventional and Motorola Type II trunked systems, encoding the voice using 12kbps CVSD and encrypting the bitstream. It is easily identified by the 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz tone at the end of transmission. As it is not 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz FCC narrowbanding mandate compliant, it does not see much use anymore. | 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 16 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 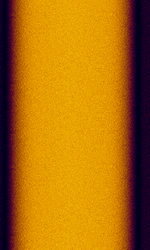 |
|
| Multiplexed Analogue Components (MAC) | Multiplexed Analogue Components (MAC/packet) family was a analogue television broadcasting standard. Replaced by digital broadcast. | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation, AMAmplitude Modulation, 2PSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), 4PSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 7.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 22 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| Multitone Paging | Multitone Paging signal, developed by Multitone Electronics in the UK. Uses similar coding to POCSAG but the headers are different and only work with Multitone's range of paging products | 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 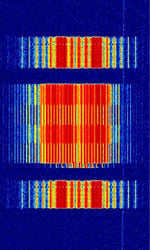 |
|
| NATEL | NATEL is a 5-tone selcall mode defined by Scandinavian National Telephone recommendations. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 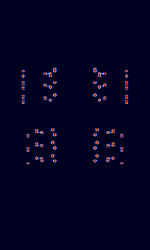 |
|
| NFM Voice | Used in analog walkie-talkies and communication systems. | 27 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 864 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 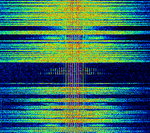 |
|
| NTSC Broadcast | National Television System Committee (NTSC) Television broadcast is an analogue television broadcast mode. Currently being phased out in parts of the world in favor of digital broadcast. | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 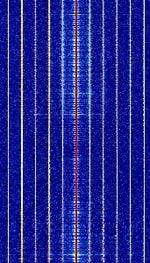 |
|
| National Public Alerting System (NPAS) | The National Public Alerting System (NPAS), branded to consumers as Alert Ready, is a national warning system in Canada. The tone does not carry any information to be decoded. Information about Emergencies is communicated via on screen text and text-to-speech. | Canada | 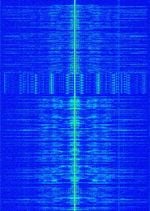 |
|||||
| Next Generation Digital Narrowband (NXDN) | NXDN is a digital narrowband trunked radio protocol used in commercial, business & industry, transport and Public Safety professional radio systems. | 136 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 520 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 6.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 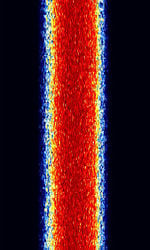 |
|
| OOK RC Car Remote Control | Cheap RC Cars with only for buttons (Forward, Reverse, Left, Right) Typically use 27Mhz or 49Mhz as the transmit frequency. There's typically no channel switching system on the remote control, which leads to interference with operating two RC vehicles at once. | 27 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 49 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 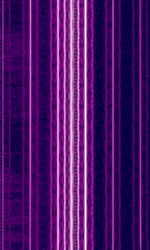 |
|
| OPERA Beacon and Data | OPERA Ad-Hoc Data/Beacon. The system is unique in that utilizes a serial data stream and Manchester coding, its therefore impossible to lose lock and its extremely robust in disturbed paths and heavy static. | 136 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 10,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 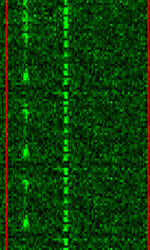 |
|
| OrbComm Mobile Telephony | Orbcomm digitized mobile satellite-based telephone signal intercepted over Hawaii, preceding NOAA 19 pass. | 137.2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 137.46 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 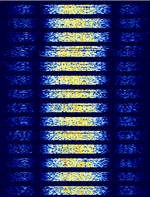 |
||
| Orbcomm | Orbcomm satellites are used for monitoring and sending short text messages. | 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | SDPSK | 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 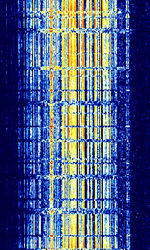 |
|
| PACKET | Packet, also known as FSK300, AFSK1200, BPSK300, QPSK600, BPSK1200, QPSK2400, AX.25 and IL2P, is a packet based protocol derived from X.25 and HDLC computer network protocols. Packet radio is a synchronous system in which data is transmitted in frames. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 730 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 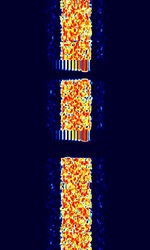 |
|
| PAL Broadcast | Phase Alternating Line (PAL) Analogue Television Broadcast. Now phased out in most of the world. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 862 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 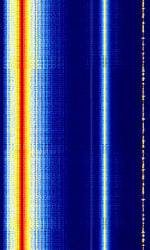 |
|
| PAX | PAX and PAX2 are developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE in 2005, and was derived from Olivia. It utilizes the AX.25 protocol that PACKET uses, and had a minimum SNR of -10dB. Can transmit APRSAutomatic Packet Reporting System, an amateur radio-based system for real time tactical digital communications of information of immediate value in the local area frames. | 3.59 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.62 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 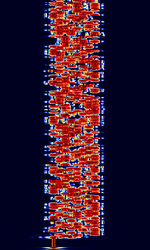 |
|
| PI4 | PI4 (PharusIgnis4) is a 4-MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying mode designed for amateur radio beacons. It is designed to work via different propagation modes. | 28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,296 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 709 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 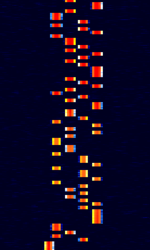 |
|
| POCSAG | POCSAG (Post Office Code Standardisation Advisory Group), also known as Super-POCSAG, Radio Paging Code No. 1 or RPC1, is a one-way 2FSK paging protocol that supports 512, 1200, and 2400 bpsBits per second (bps). | 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 932 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 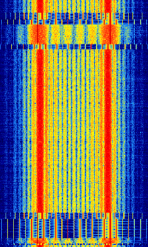 |
|
| PSK Paging link | Also known as PSKPhase-Shift Keying paging, is a signal that allows side-by-side PSKPhase-Shift Keying to exist in AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying paging links, allowing for more dynamically processed DSP available. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 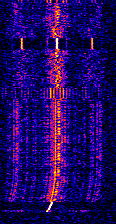 |
|
| PSK-AM | PSKPhase-Shift Keying-AMAmplitude Modulation is an amateur digital mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE in 2002/2003, and incorporates FECForward Error Correction interleaving. PSKPhase-Shift Keying-AMAmplitude Modulation uses the modulation of PSK10/31 with the FECForward Error Correction of SITOR-B. | 10.148 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.62 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 40 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 180 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| PSK2K | PSK2K is a meteor scatter type of mode written by DJ5HG Using a modulation scheme of BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) at 2000 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 50.36 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.36 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 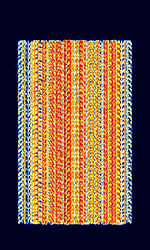 |
|
| Phase Shift Keying (PSK) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying is a digital teletype mode based on Phase-Shift Keying (PSKPhase-Shift Keying) modulation. The most popular amateur radio PSKPhase-Shift Keying mode is PSKPhase-Shift Keying 31. | 1.838 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 909 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 10 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 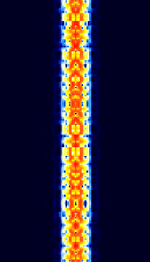 |
|
| Portable Traffic Lights | Signals sent from portable traffic lights that are often used at roadworks. | 154.463 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | Worldwide | 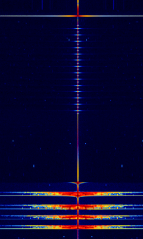 |
|||
| Positive Train Control (PTC) | Positive train control (PTC) is a system of functional requirements for monitoring and controlling train movements as an attempt to provide increased safety. | 220 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 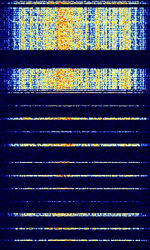 |
||
| Primex Wireless Time Sync | Primex Wireless Time Sync is a VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) Time Synchronization signal used in Primex Wireless's XR Series. | 72.02 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 72.98 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 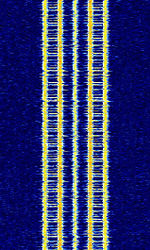 |
|
| ProVoice | ProVoice is a digital voice mode used in EDACS trunked systems. | 160 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | Worldwide | 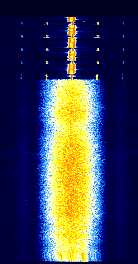 |
||
| Project 25 (P25) | Project 25 (P25 or APCO-25) is a trunked radio standard developed by The Association of Public Safety Communications Officials International (APCO-25) for use with public safety organizations around the world. | 136 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 939 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, C4FMContinuous 4-Level Frequency Modulation, TDMATime Division Multiple Access | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 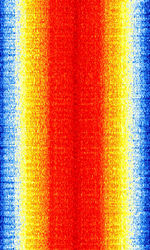 |
|
| Pulse Coded Modulated (PCM) RC Toy | Signal used for remote control (RC) Toys. | 27.145 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 49 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | PCM | Worldwide |  |
|||
| Q65 | Q65 is a 65-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying extreme weak-signal mode which is designed for Earth-Moon-Earth communications and fast-fading propagation modes such as tropospheric scatter, rain scatter and trans-equatorial propagation. It offers a variety of submodes. Q65 is part of the WSJT-X software. | 50.275 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 144.17 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 19 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.733 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Quansheng UVK5 Digital Text Message | A digital text message protocol included in the stock firmware of some Quansheng brand handheld radios to send up to 30 characters in a short packet type message. | 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 480 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 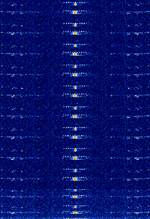 |
|
| Radio Data Link Access Procedure (RD-LAP) | Motorola's Radio Data Link Access Procedure (RD-LAP) is a 1G protocol that was used in ARDIS and DataTAC Networks, and is still used in some MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office.'s, as well as gas companies, police departments, fire departments, financial companies, etc. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 850 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 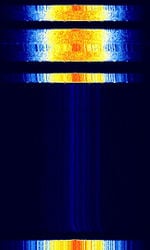 |
|
| Radio Data System (RDS) | Radio Data System (RDS) and its North American variant, Radio Broadcast Data System (RBDS), are data modes transmitted on subcarriers of commercial FMFrequency Modulation radio station transmissions. | 65 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | DSBDual Side Band Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 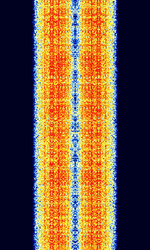 |
|
| Rain Master sprinkler control | Control signal for grass sprinkler watering system | 154.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 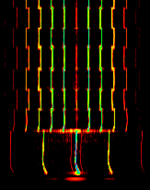 |
|
| Road Coordination/Maintenance Telemetry | A sort of SCADA signaling method used to cooordinate traffic or other road works using external NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation transmitters. Can also be shared with road commission vehicles and related things. | 151.01 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 6.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 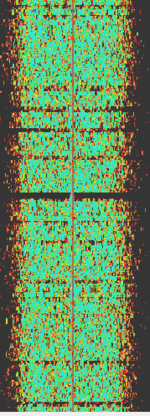 |
|
| SECAM | Sequential Colour with Memory (SECAM) Analogue Television Broadcast. Now phased out in most of the world. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 862 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 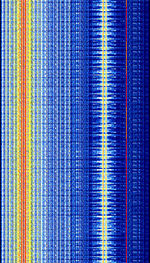 |
|
| SECOR 4 (EGRS 4) | SECOR 4 (COSPAR ID: 1965-027B) was a SEquential COllation of Range series satellite, and is occasionally active when receiving adequate solar power on it's panels. It is not consistent, likely owing to a tumbling or rotating motion. | 136.845 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IRIG | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz |  |
||
| SIMONe meteor radar | The SIMONe radar is a meteor detection system that is operated in multiple research sites around the world. It uses continuous spread-spectrum coded transmissions which gives it an unusual sound when demodulated into audio. It can be received over long distances during sporadic-E and other special propagation conditions. | 32.55 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, DSSS | 140 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 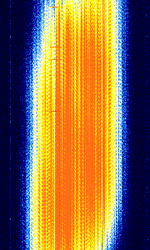 |
|
| SKiYMET meteor radar | SKiYMET is a meteor detection radar which is used by many research institutes around the world. It can use different transmission parameters and can be received over long distances during sporadic-E and other special propagation conditions. | 29 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 40 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | Pulsed | 160 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 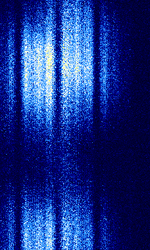 |
|
| SNOTEL (Snow Telemetry) | SNOTEL stations are a set of precipitation and other sensors spread across the mountains of the United States by the Department of Agriculture through the National Resources Conservation Service. | 40.67 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 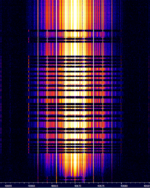 |
|
| SNOTEL (Snow Telemetry) | SNOTEL stations are a set of precipitation and other sensors spread across the mountains of the United States by the Department of Agriculture through the National Resources Conservation Service. | 40.67 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States |  |
|
| SOLRAD 7B (COSPAR ID: 1965-016D) | SOLRAD-7B is one of the many "zombie satellites" in orbit and is an artifact of the mid 1960's US space program. It occasionally will become active again when illuminated by sunlight due to the satellite bus having several small, semi-circular solar panels. | 136 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 136.806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | AMAmplitude Modulation IRIG | 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 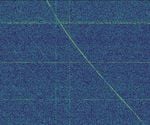 |
||
| STP403 Bus PIT System | STP403 is a bus PITPassenger Information Terminals, such as bus timetable displays at bus stops system used to update digital displays at bus stops. STP403 was developed by French companies INEO and CESATEC. | 164 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 468.488 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | France | 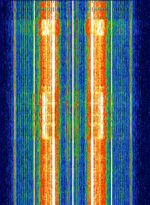 |
|
| Siemens 1.5T MRI Scanner | Radio signal used by MRI machines to excite protons and obtain their response. | 64 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 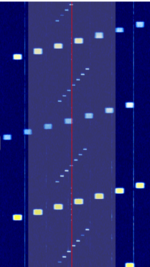 |
||||
| Slow-Scan Television (SSTV) | Slow-scan television (SSTV) is a method for picture transmission used by amateur radio operators to transmit and receive images. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables), LSBLower Side Band Modulation, NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 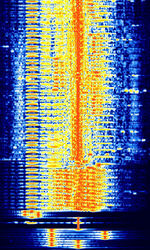 |
|
| Soyuz-MS spacecraft telemetry | Russian spacecraft telemetry system. | 166 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 634 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PCM, FMFrequency Modulation | 250 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 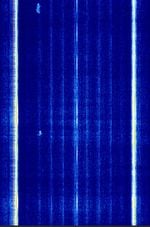 |
|
| Switching Electronic Interference | Commonly experienced interfering RFRadio Frequency emissions from switching electronics (i.e. switched-mode power supplies, power converters, digital electronics, etc.) which use inductors (coils) that unintentionally act as antennas. | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 200 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 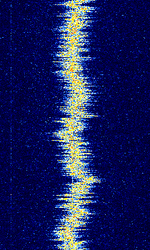 |
||||
| Traffic Light Control R09 | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying Modulated signal with 2400Baud for traffic light control. Contains R09.16 telegrams as specified per VDV Standard 420. | 68 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Germany | — | 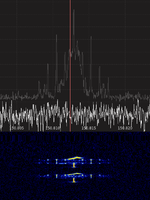 |
|
| Transit 5B-5 | Transit 5B-5, a former TRANSIT navigation satellite, is the oldest satellite known to still transmit a signal. Considered "dead" because its navigational systems failed after 19 days of operation, it still emits a telemetry signal when illuminated. | 136.658 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | PCM, PAMPulse Amplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation, PM | 32 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 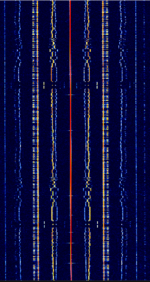 |
|
| UHF Vehicle Location System | UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) Vehicle Location System | 400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 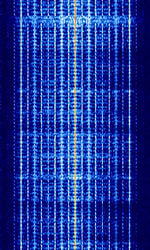 |
|
| VDEW | VDEW is a 5-tone selcall mode defined by the Vereinigung Deutscher Elektrizitaetswerke in Germany. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| VHF Data Link - Mode 2 (VDL-M2) | VDL-M2 (Known as VDL2 or VDLM2) is a means of sending information between aircraft and ground stations. VDL Mode 2 is the only VDL mode being implemented operationally to support Controller Pilot Data Link Communications (CPDLC). An extension to the AVLC protocol permits ACARS over AVLC (AOA) transmissions. VDL-M2 is implemented by Eurocontrol. | 117.975 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 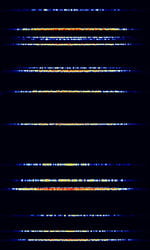 |
|
| VHF Omnidirectional Range (VOR) | A type of radio navigation system used by aircraft. It is distinctive in that the center frequency is flanked by two FMFrequency Modulation waves. | 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 117.95 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 21 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 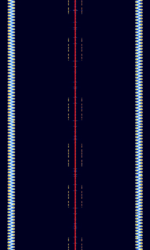 |
|
| VOICE | VOICE is a MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE in 2006, and was derived from Olivia. It was designed for blind or partially sighted amateur radio operators. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 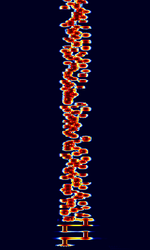 |
|
| Voice Inversion Scrambling | Analog Voice Inversion Scrambling divides the spectra into multiple bands and swaps them. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 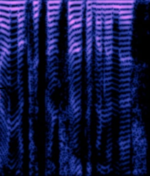 |
|
| WSPR | Weak Signal Propagation Reporter. | 136 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1,296.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 6 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 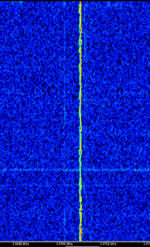 |
|
| Wettersonde E084 (Radiosonde) | The E084 is a radiosonde designed in 1990 by Deutsche Wetterdienst. It broadcasts a temperature reading at 403.05 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz via a FMFrequency Modulation-modulated tone which changes pitch depending on the temperature. | 403.05 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 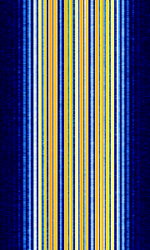 |
|
| WinLink Global Email Radio System (WGERS) | Winlink, a email service over radio that uses internet connected gateways in order to provide position reporting, weather and information bulletins. It is used for disaster-relief. | 7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables), NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 2MFSK, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, PSKPhase-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 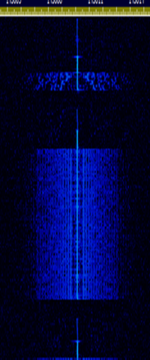 |
|
| Yaesu System Fusion | System Fusion is Yaesu's digital voice/data protocol for amateur radio, using the AMBE+2 vocoder on a C4FMContinuous 4-Level Frequency Modulation signal. | 144 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | C4FMContinuous 4-Level Frequency Modulation | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 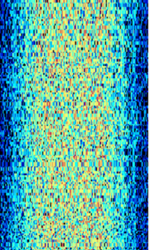 |
|
| ZVEI Selcall | ZVEI is a family of selcall modes defined by the Zentralverband der Electrotechnischen Industrie in Germany. Selcall modes include ZVEI-1, ZVEI-2, ZVEI-3, PZVEI, DZVEI, PDZVEI and ZVEI-VDEW. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 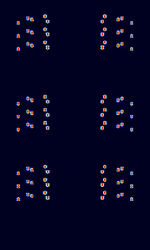 |
|
| Électricité de France HNZ | Electrical substation SCADA protocol used by EDF (Électricité de France). | 68.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 73.3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying | 8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | France |  |
Pages in category "VHF"
The following 167 pages are in this category, out of 167 total.