Low Frequency (LF)
From Signal Identification Wiki
(Redirected from LF)
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) encompasses frequencies from 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz to 300 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Accurate positioning by Low Frequencies (ALF) | Accurate positioning by Low Frequencies, a former German DGPS navigation system. No longer in use as of 2013. | 123.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Germany | 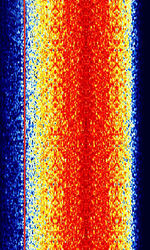 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation (AM) | Long range commercial broadcast and international radio. Also used for aviation communications. | 153 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 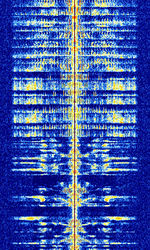 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) | Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) is a DRM-based radiotext and data technology for AMAmplitude Modulation broadcasting, like RDS that is used for FMFrequency Modulation. It transmits as a subcarrier, phase-modulating the carrier frequency. | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | 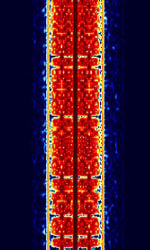 |
||
| BPC | BPC is the callsign of the Chinese low-frequency time broadcasting station, located near Shangqiu, Henan in China. | 68.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | AMAmplitude Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | China | 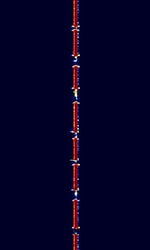 |
|
| Coherent BPSK | Coherent BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), also known as C-BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), was an experimental amateur mode developed by Bill DeCarle VE2IQ. | 138 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 18.081 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 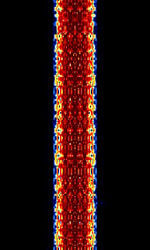 |
|
| DCF77 | DCF77 is a German longwave time signal radio station based at 77.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz. DCF uses an AMAmplitude Modulation modulated carrier and phase modulation sidebands to transmit its time signal. | 77.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Germany | 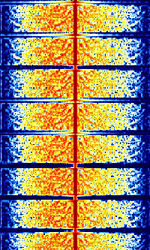 |
|
| Differential Global Positioning System (DGPS) | Differential GPS (DGPS), also known as M823 DGPS and SC-104 DGPS, is a supplementary correction signal used by GPS receivers to increase the accuracy of GPS based positioning. | 283.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.95 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 150 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 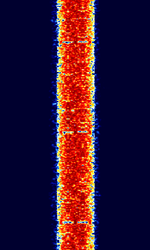 |
|
| EFR Teleswitch | Europäische Funk-Rundsteuerung (EFR) Teleswitch (European Radio Ripple Control GmbH (ERA) Teleswitch) is an energy management system operated via long-wave radio. Uses two transmitters in Germany and one in Hungary. Also known by DCF39, DCF49 and HGA22. | 129.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 139.9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe |  |
|
| FST4 | FST4 is a 4-GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying amateur radio communications mode, designed especially for making contacts (QSO's) on LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) and MFMedium Frequency (300-3000 kHz) frequency ranges under extreme weak-signal conditions. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | 137 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 474 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 0 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 66 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 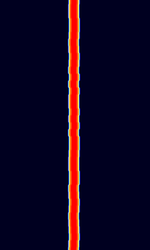 |
|
| FST4W | FST4W is an amateur radio digital protocol designed particularly for the LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) and MFMedium Frequency (300-3000 kHz) bands, for quasi-beacon transmissions of WSPR-style messages. FST4W uses 4-GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying modulation and offers T/R sequence lengths of 120, 300, 900, and 1800 seconds. | 136 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.839 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 0 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 5 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 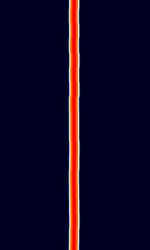 |
|
| GYN2 GBR | Transmitting site owned by the Ministry of Defense. Originally constructed in 1946 and was originally used as a shortwave radio station. In present time, the transmitting site is used by the British Navy in order to transmit encrypted messages to submarines at sea. The site is also capable of DRM and is beamed at 121°, towards Germany and Central Europe | 81 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United Kingdom | 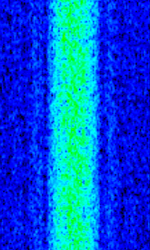 |
||||
| Induction cooker interference | RFRadio Frequency interference from nearby induction cooker can sometimes be mistaken for a real LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) or VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) transmission. | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | Worldwide | 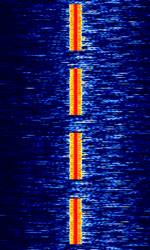 |
|||
| JJY | JJY, also known as JJY-40 and JJY-60, is the call sign for a pair of longwave Time Signal stations in Japan. | 40 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 60 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | AMAmplitude Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Japan | 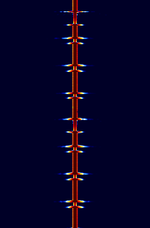 |
|
| JT9 | JT9 is a 9-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode for making contact (QSO's) under extreme weak-signal conditions. It is part of the WSJT-X software. | 3.578 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.079 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 16 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 1.78 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 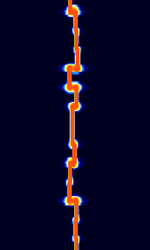 |
|
| LORAN | LORAN (short for LOng RAnge Navigation) is a hyperbolic radio navigation system. | 90 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 110 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PPMPulse Position Modulation | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 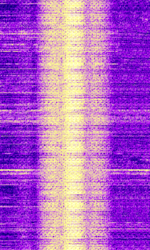 |
|
| Lentus | Lentus is an extremely slow QRPIn amateur radio, QRP operation refers to transmitting at reduced power while attempting to maximize one's effective range. mode developed by Patrick Lindecker F6CTE used to transmit QRPIn amateur radio, QRP operation refers to transmitting at reduced power while attempting to maximize one's effective range.'s at very low power. Each 43-character (75 bit) transmission takes roughly 5 minutes to transmit across 32 possible tones in a tight 25 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). bandwidth. | 136.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 14.096 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 25 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 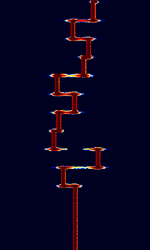 |
|
| MSF | MSF is a time signal station in Anthorn, United Kingdom, which broadcasts the UK national time reference | 60 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 5 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United Kingdom, Europe | 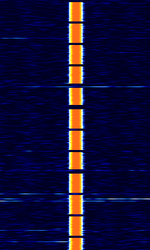 |
|
| Morse Code (CW) | CWContinuous Wave Morse Code is the simplest form of transmission found virtually all over the RFRadio Frequency bands for a variety of uses. The most common use of this is for Call-sign Beacons by both Amateur and Military operators. | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 250,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | Worldwide |  |
||
| NDB beacon signals | Non-directional Beacons are low frequency navigation aids | 290 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 421 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Brussels, Belgium | 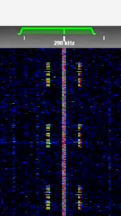 |
||
| Non-Directional Beacon (NDB) | A Non-Directional Beacon (NDB) is a ground-based, low frequency radio transmitter used as an instrument approach for airports and offshore platforms. | 190 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | AMAmplitude Modulation | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| RBU | RBU is a time code radio station located in Moscow. It transmits a continuous 10 kW time code on 66.66 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz. | 66.66 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 650 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 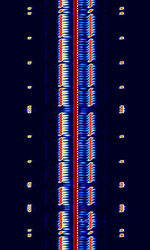 |
|
| Radio Teletype (RTTY) | RTTYRadio TeleTYpe (Also known as Baudot or ITA2) uses the Baudot 5-bit alphabet with FSKFrequency-Shift Keying to send text messages over the shortwave. This mode is gradually dying out in favor of more robust modes like PSK31 in the amateur service. | 147.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 28.15 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 850 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Russian overhead power line telemetry system | Russian telemetry system, transmitted over the overhead power lines. | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 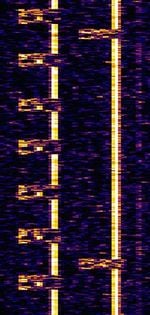 |
|
| SAS/SRC | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio) | 40.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 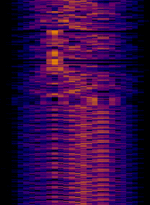 |
|||
| SAS2 | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio) and is activated less often as the other Swedish transmitters used for VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) submarine communication. Usually, it works with reduced power. | 42.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 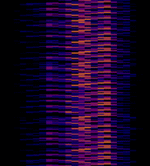 |
|||
| SAS3 | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio). | 44.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 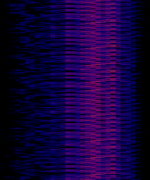 |
|||
| SHR | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio). | 38 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 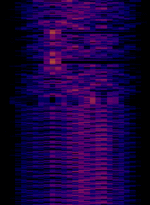 |
|||
| STANAG 5065 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 5065 is defined as "Minimum Standards for Naval Low Frequency (LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz)) Shore-To-Ship Surface Broadcast Systems", with two primary protocols, FSK75 and MSK300. | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 160 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 235 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 360 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Single frequency russian overhead power line telemetry system | Russian telemetry system, transmitted over the overhead power lines. | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 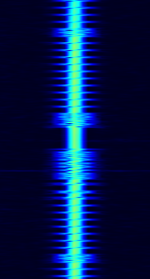 |
|
| Sonne | Sonne (Called Consol by the Britons) was a low-frequency radio range based radio navigation system used for long range navigation. | 250 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 350 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 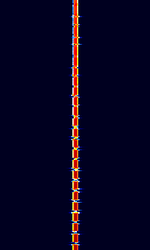 |
|
| Switching Electronic Interference | Commonly experienced interfering RFRadio Frequency emissions from switching electronics (i.e. switched-mode power supplies, power converters, digital electronics, etc.) which use inductors (coils) that unintentionally act as antennas. | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 200 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 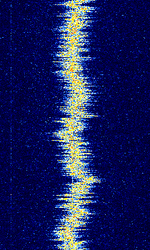 |
||||
| TDF | TDF, also known as ALS162, is a time signal transmitted on the former carrier of France's France Inter longwave AMAmplitude Modulation radio station on 162 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz. | 162 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | France | 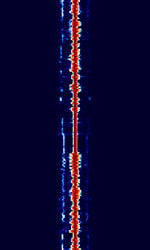 |
|
| UK AM Data System (UK-AMDS) | UK AMAmplitude Modulation Data System (UK-AMDS) was developed by BBC Research and Development in 1984 as a way to transmit low bitrate data on BBC Radio 4's LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) AMAmplitude Modulation carrier. Elements of this system were adopted into ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards.'s AMSS. | 198 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United Kingdom | 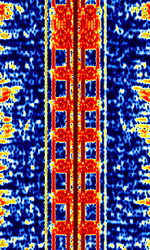 |
|
| WSPR | Weak Signal Propagation Reporter. | 136 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1,296.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 6 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 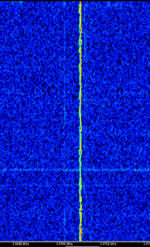 |
|
| WWVB | WWVB is the lowest frequency time signal in the USA. | 60 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 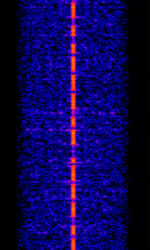 |
Pages in category "LF"
The following 37 pages are in this category, out of 37 total.