Marine
From Signal Identification Wiki
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ARQ-M2-242 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M2-242 (Also known as TDM 242, TDM-2, 96-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-28) is a two-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 242 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Marine, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 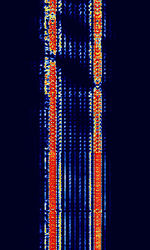 |
|
| ARQ-M2-342 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M2-342 (Also known as TDM 342, TDM-2, 96-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-28) is a two-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 342 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Maritime, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 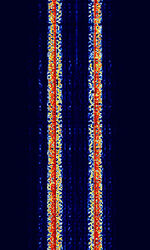 |
|
| ARQ-M4-242 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M4-242 (Also known as TDM 242, TDM-4, 192-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-56) is a four-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 242 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Maritime, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 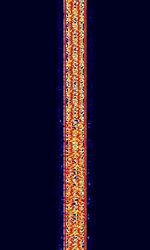 |
|
| ARQ-M4-342 | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-M4-342 (Also known as TDM 342, TDM-4, 192-TDM, and ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-56) is a four-channel time division multiplexed telex system. This is the CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 342 standard version. Used in Aeronautical, Maritime, and Point-to-Point services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 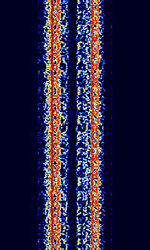 |
|
| Automatic Identification System (AIS) | Automatic Identification System (AIS) is used by ships to broadcast position and vessel information. | 161.975 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 162.025 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 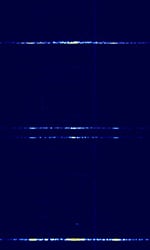 |
|
| Automatic Transmitter Identification System (ATIS) | ATIS systems are identification tags used by inland commercial waterway traffic on rivers in Europe. The FSKFrequency-Shift Keying burst is appended at the end of every voice transmission by the vessel operator. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 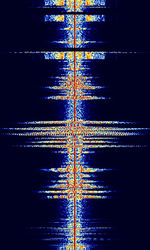 |
|
| BRAS-3 (RS-10) | BRAS-3 and the closely related RS-10 are Russian medium frequency hyperbolic navigation systems used for marine navigation | 1.685 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 2.107 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, Pulse | 14 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 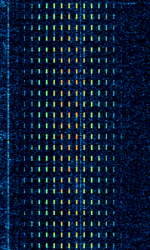 |
|
| CODAR | CODAR (Coastal Ocean Dynamics Applications Radar) is used for near-surface ocean monitoring, such as waves and water current. | 4.438 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 42.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | ILFM | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 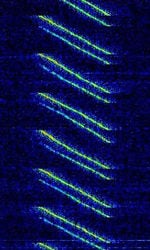 |
|
| CRY2001 Voice Scrambler | CRY2001 is a voice scrambling mode used on Sailor CRY2001 Scramblers. Fisherman often use these modes to communicate with privacy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 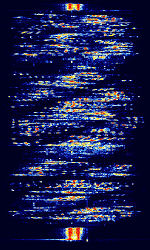 |
|
| Datawell Buoy HF Link | Datawell Buoy HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Links transmitted by Datawell Marine measurement buoys, measuring ocean conditions, temperature, and wave current. | 25.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 45 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 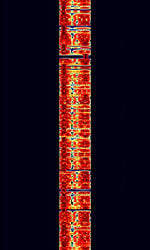 |
|
| DeltaFix | DeltaFix was a DGPS system that was used to provide precision positioning used in the survey and oceanographic industry. | 1.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 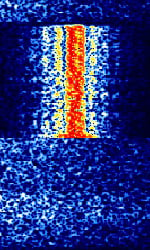 |
|
| Distress Radiobeacon (Analog) | Analog Distress Radiobeacons are simple siren-based transmitters that were installed in older EPIRB's, PLB's and ELT's. Currently used as a supplementary homing signal in modern digital radiobeacons. | 121.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 243 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | ||
| Distress Radiobeacon (Digital) | Digital Distress Radiobeacons (EPIRB's, PLB's and ELT's) are emergency radio beacons used for search and rescue operations to locate a vessel, plane, or person in distress. | 406 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 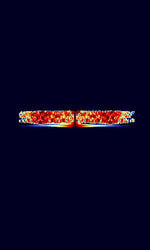 |
|
| Driftnet Buoy Radio Beacon | Driftnet Radio Buoys are extensively used by fishing boats operating in open seas and oceans for collecting long fishing lines or fishing nets, with the assistance of a radio direction finder | 1.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 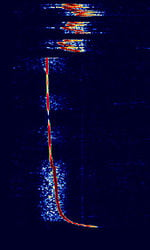 |
|
| GMDSS Digital Selective Calling | Global Maritime Distress and Safety System's Digital Selective Calling (GMDSS-DSC) is a maritime communication protocol intended to initiate ship-to-ship, ship-to-shore and shore-to-ship radiotelephone and MFMedium Frequency (300-3000 kHz)/HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) radiotelex calls. | 2.177 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 156.525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 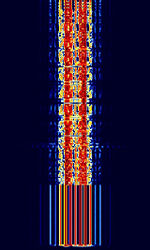 |
|
| Globe Wireless HF Network | Globe Wireless' Maritime Digital Radio was a system of 24 stations around the globe offering data services to large cargo vessels. Since 2014, GW has discontinued their HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) network. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| HyperFix | HyperFix was a radio-navigation system developed by Racal. Was used by vessels and ships. Has largely been phased out in favor of Differential GPS. | 1.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 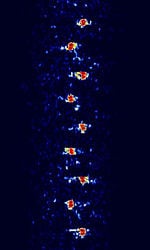 |
||
| Inmarsat IsatM2M | IsatM2M Service operated by Inmarsat on existing Inmarsat-D/D+ infrastructure. | 1,525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,559 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.024 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 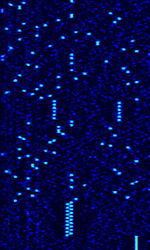 |
|
| Inmarsat-C TDM | Inmarsat C provides two-way data and messaging communication services to and from virtually anywhere in the world. The low-cost terminals and antennas are small enough to be fitted to any size of ship. | 1,537.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,539.685 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 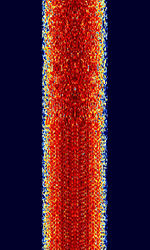 |
|
| Inmarsat-D(D+) Downlink | Inmarsat D+ (and it's predecessor, Inmarsat D) was Inmarsat's satellite paging system. The main use of the technology was in tracking trucks and buoys and SCADA applications. | 1,525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,559 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 640 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| LORAN | LORAN (short for LOng RAnge Navigation) is a hyperbolic radio navigation system. | 90 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 110 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PPMPulse Position Modulation | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 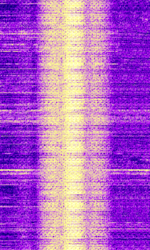 |
|
| Podsolnukh 'Sunflower' Radar | A Russian over the horizon radar, also known as "Sunflower" | 3.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis. | FMOP | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia, Worldwide |  |
|
| SAS/SRC | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio) | 40.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 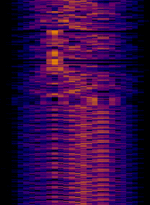 |
|||
| SAS2 | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio) and is activated less often as the other Swedish transmitters used for VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) submarine communication. Usually, it works with reduced power. | 42.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 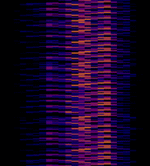 |
|||
| SAS3 | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio). | 44.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 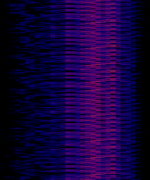 |
|||
| SHR | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio). | 38 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 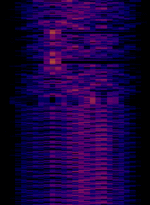 |
|||
| SITOR-A | SITOR-A (Also known as AMTOR-A) is one of two modes of SITOR, which stands for Simplex Teletype Over Radio. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 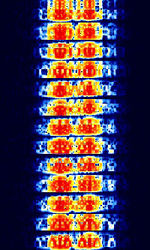 |
|
| SITOR-B | SITOR-B is one of two modes of SITOR (Simplex Teletype Over Radio). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 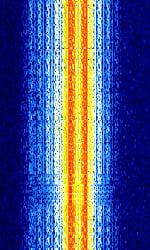 |
|
| Sonne | Sonne (Called Consol by the Britons) was a low-frequency radio range based radio navigation system used for long range navigation. | 250 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 350 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 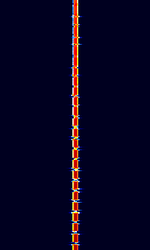 |
|
| WLO | AMAmplitude Modulation | CWContinuous Wave | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States |  |
Pages in category "Marine"
The following 32 pages are in this category, out of 32 total.
A
BCD |
D cont.GHILP |
SUW |