Analogue Signals
From Signal Identification Wiki
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1G (NMT) Nordic Mobile Telephone | Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT, NMT-450, and NMT-900) is a first generation analog cell phone system. Originally designed for and by Nordic countries (Finland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark) it was widely deployed around the world. Nowadays (as of 2015) NMT is defunct. | 453 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 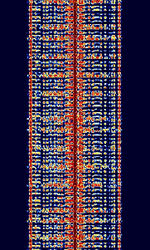 |
|
| 1G Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) | The first generation of cellular mobile telecommunications, which used analogue NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation voice. | 824 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 894 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 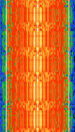 |
|
| Altai Radiotelephone | The initial generation of cellular mobile radiotelecommunications, similar to trunked radio. -- (Audio Sample is *loud*) -- | 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 342 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 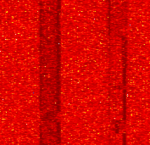 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation (AM) | Long range commercial broadcast and international radio. Also used for aviation communications. | 153 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 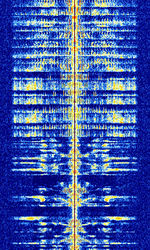 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) | Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) is a DRM-based radiotext and data technology for AMAmplitude Modulation broadcasting, like RDS that is used for FMFrequency Modulation. It transmits as a subcarrier, phase-modulating the carrier frequency. | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | 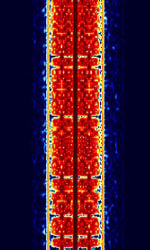 |
||
| Automatic Picture Transmission (APT) | Automatic Picture Transmission (APT), also known as NOAA-GEOSAT, was an analog image transmission mode used by the NOAA weather satellites and some Russian weather satellites to transmit satellite weather photos. As of august 2025, most of the NOAA sats that transmitted this mode have been decommissioned, and have discontinued transmission. | 137.1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 137.913 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 34 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 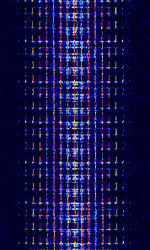 |
|
| CCIR Selcall | CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) selcall consists of CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R)-1, CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R)-2, and PCCIR, which are 5-tone selcall modes for VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz)/UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) radios. CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R)-1 and CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R)-2 only differ in the tone duration, and PCCIR only differs in the group, reset, and repeat tone frequencies. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 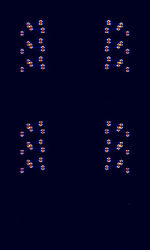 |
|
| CRY2001 Voice Scrambler | CRY2001 is a voice scrambling mode used on Sailor CRY2001 Scramblers. Fisherman often use these modes to communicate with privacy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 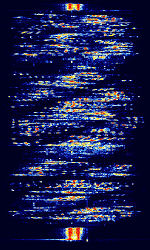 |
|
| DB0UPB research beacon | The is a research beacon for training neural networks. | 3.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.101 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | LSBLower Side Band Modulation, USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, LSBLower Side Band Modulation, USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Germany | 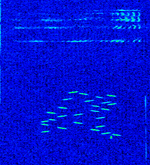 |
|
| Distress Radiobeacon (Analog) | Analog Distress Radiobeacons are simple siren-based transmitters that were installed in older EPIRB's, PLB's and ELT's. Currently used as a supplementary homing signal in modern digital radiobeacons. | 121.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 243 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | ||
| Dual Tone Multi Frequency (DTMF) | DTMF is a signaling mode used for a variety of purposes. It's most known for telephony dialing, but is in use for many different applications such as DTMF paging for DTMF-enabled VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz)/UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) radios. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 3.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| EURO | EURO is a 6/7-tone selcall mode used in VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz)/UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) radios. Also known as EuroSignal. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Eurobalise downlink | Downlink from train to balise. A Eurobalise is a specific variant of a balise, a transponder placed between the rails of a railway. | 27.095 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | Europe | 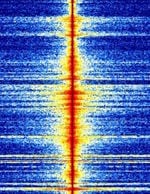 |
|||
| FM Broadcast Radio | Commercial Broadcast FMFrequency Modulation radio stations. Used for the broadcast of many different radio programs, including music, news, sports, weather, and talk shows. | 65 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 38 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 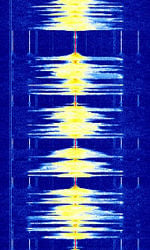 |
|
| FM NBTV | FMFrequency Modulation NBTV is a method to send moving images in a very narrow bandwidth (maximum 3 KHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz) | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 2.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 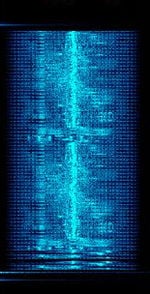 |
|
| Hellschreiber | Hellschreiber (Also known as Feld Hell or just Hell) is a teleprinter system developed in the late 1920's by Rudolf Hell, a German inventor. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 350 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 800 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 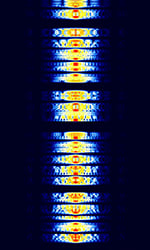 |
|
| Horus Binary 4FSK - v2 | An efficient RTTYRadio TeleTYpe-like 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying mode that transmits binary data, used for amateur high altitude balloon telemetry. Developed by the Project Horus group. | 431 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 434 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 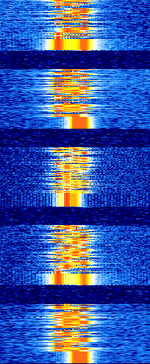 |
|
| ICAO Selcal | ICAO Selcal (also known as AVCALL, ANNEX 10, or just SELCAL) is a HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz)/VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) aviation selective calling system used by ground stations to initiate radio communications with aircraft. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 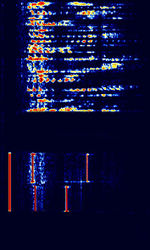 |
|
| Ionized Meteor Trails | Meteors traversing the E region of the atmosphere approximately 60 - 90 miles up create ionizing trails which can reflect and refract radio waves from commercial FMFrequency Modulation radio stations that are hundreds and sometimes thousands of miles away from the receiver. | 88.3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | CWContinuous Wave | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 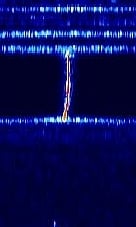 |
|
| Kenwood FleetSync | FleetSync is a manufacturer specific signaling standard which includes a number of features: unit ID, status, emergency button, inhibit, status check, GPS, and selective calling. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 850 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | — | 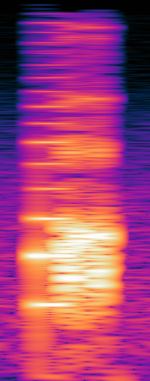 |
|
| MFJ-269C Antenna SWR Analyzer | Popular antenna analyzer among ham operators and the like. Output power is only ~20mW so if heard, source is nearby. Other MFJ models may be similar. | 500 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 500 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation, NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 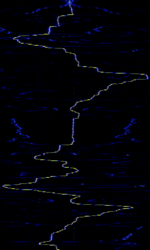 |
||
| Meteosat WEFAX | Meteosat WEFAX is a WEFAX used to transmit satellite images via Meteosat Satellites. WEFAX was introduced with the first Meteosat in 1977. | 1,691 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | Worldwide | 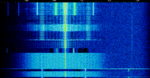 |
||
| Multiple sub-Nyquist Sampling Encoding (MUSE) | Multiplite sub-Nyquist Sampling Encoding (MUSE) also known as Hi-Vision was a early analogue high-defition television standard developed by NHK Science and Technical Research Laboratories. Replaced by digital ISDB broadcast since 2007. | 8,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 12,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | FMFrequency Modulation, DPCM, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation | 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 27 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| Multiplexed Analogue Components (MAC) | Multiplexed Analogue Components (MAC/packet) family was a analogue television broadcasting standard. Replaced by digital broadcast. | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation, AMAmplitude Modulation, 2PSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), 4PSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 7.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 22 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| NFM Voice | Used in analog walkie-talkies and communication systems. | 27 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 864 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 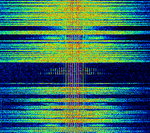 |
|
| NOAA ITOS High Resolution Picture Transmission (HRPT) | An analog signal broadcast from NOAA ITOS polar satellites that transmitted images from the VHRR radiometer. | 1,697.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 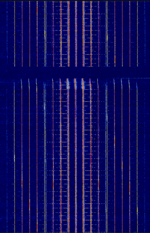 |
|
| NTSC Broadcast | National Television System Committee (NTSC) Television broadcast is an analogue television broadcast mode. Currently being phased out in parts of the world in favor of digital broadcast. | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 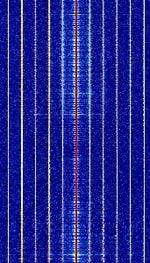 |
|
| National Public Alerting System (NPAS) | The National Public Alerting System (NPAS), branded to consumers as Alert Ready, is a national warning system in Canada. The tone does not carry any information to be decoded. Information about Emergencies is communicated via on screen text and text-to-speech. | Canada | 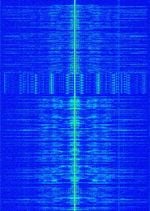 |
|||||
| OFDM NBTV | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing NBTV is an analog technique, in fact it is a true Fuzzy design as well. The transmission technique used is quite different from conventional TV | 3 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | Analog OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 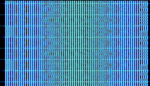 |
|
| OTP-2 Satellite Musical Beacon | Musical transmission originating from the OTP-2 Cubesat | 400.502 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 4.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 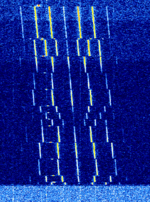 |
|
| PAL Broadcast | Phase Alternating Line (PAL) Analogue Television Broadcast. Now phased out in most of the world. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 862 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 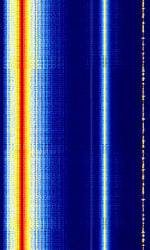 |
|
| Primary Aeronautical Surveillance Radar | A Primary radar (PSR Primary Surveillance Radar) is a conventional radar sensor that illuminates a large portion of space with an electromagnetic wave and receives back the reflected waves from targets within that space. | 1,215 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | Pulse | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 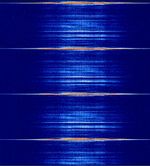 |
|
| Radar altimeter | Aircrafts radar altimeter. | 4,200 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 4,300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | FMCW | 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 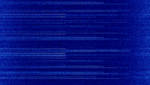 |
|
| S-Band Jammer | This is what the signal of a military S-Band (In this case 2.4 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz) RADAR and WiFi intentional interference (Jamming) device looks like. This signal is generated by a DDS system and is then used to modulate the output of a 2.45 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz magnetron (The same as in a microwave oven). | 2,400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Noise | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 100 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
|
| SECAM | Sequential Colour with Memory (SECAM) Analogue Television Broadcast. Now phased out in most of the world. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 862 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 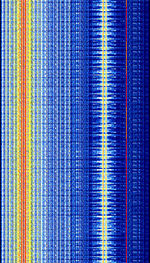 |
|
| SECOR 4 (EGRS 4) | SECOR 4 (COSPAR ID: 1965-027B) was a SEquential COllation of Range series satellite, and is occasionally active when receiving adequate solar power on it's panels. It is not consistent, likely owing to a tumbling or rotating motion. | 136.845 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IRIG | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz |  |
||
| SOLRAD 7B (COSPAR ID: 1965-016D) | SOLRAD-7B is one of the many "zombie satellites" in orbit and is an artifact of the mid 1960's US space program. It occasionally will become active again when illuminated by sunlight due to the satellite bus having several small, semi-circular solar panels. | 136 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 136.806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | AMAmplitude Modulation IRIG | 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 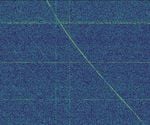 |
||
| Single Sideband Voice | Single-sideband voice is a subtype of AMAmplitude Modulation voice modulation. It is used in HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) amateur bands and for weak signal VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) and UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) voice, as well as aircraft weather reports. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 1.9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 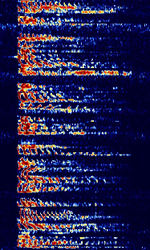 |
|
| Slow-Scan Television (SSTV) | Slow-scan television (SSTV) is a method for picture transmission used by amateur radio operators to transmit and receive images. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables), LSBLower Side Band Modulation, NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 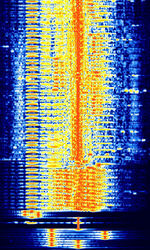 |
|
| Sonne | Sonne (Called Consol by the Britons) was a low-frequency radio range based radio navigation system used for long range navigation. | 250 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 350 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 1 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 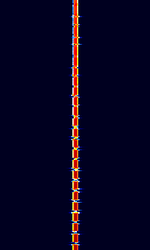 |
|
| Thales Système 3000 Voice Scrambler | Voice Scrambling mode from Thales Système 3000 HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Modem. Has characteristic PSKPhase-Shift Keying and MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying bursts at the beginning and end of a voice transmission. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| The Buzzer (ZhUOZ MDZhB UZB76) | The Buzzer, call-sign NZhTI (formerly ANVF, ZhUOZ, MDZhB and UZB-76), is a Russian Military Commandment system signal used to broadcast diplomatic ciphered messages known as "monolit" to the russian navy. If there is no message to broadcast, its "homing" signal is a loud ship-horn buzzing sound. It is believed to serve a similar purposes to The Alarm and The Air Horn. | 4.625 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 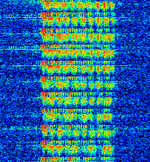 |
|
| The Goose | "The Goose" is a Russian military commandment network serving the Western Military District. It broadcasts on 4310 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz during daytime, changing to 3243 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz for nighttime. | 3.243 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 4.31 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | AMAmplitude Modulation | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 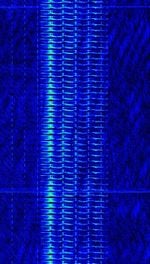 |
|
| Total Access Communication System (TACS) | A first generation analogue mobile cellular system which operated in the United Kingdom and a handful of other countries in Europe. It is also the EU's form of AMPS. | 872 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 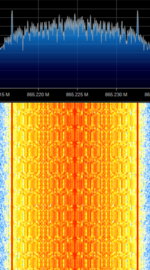 |
|
| Transit 5B-5 | Transit 5B-5, a former TRANSIT navigation satellite, is the oldest satellite known to still transmit a signal. Considered "dead" because its navigational systems failed after 19 days of operation, it still emits a telemetry signal when illuminated. | 136.658 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | PCM, PAMPulse Amplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation, PM | 32 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 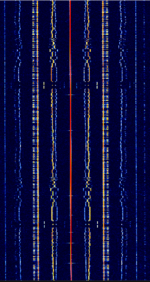 |
|
| UK AM Data System (UK-AMDS) | UK AMAmplitude Modulation Data System (UK-AMDS) was developed by BBC Research and Development in 1984 as a way to transmit low bitrate data on BBC Radio 4's LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) AMAmplitude Modulation carrier. Elements of this system were adopted into ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards.'s AMSS. | 198 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United Kingdom | 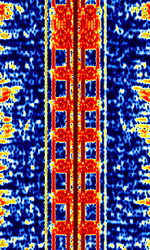 |
|
| VDEW | VDEW is a 5-tone selcall mode defined by the Vereinigung Deutscher Elektrizitaetswerke in Germany. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Vaisala RS80 | Valsala Radiosonde RS80. This is an analog weather balloon radiosonde. Measures Temperature, Pressure and Humidity. | 1,680 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 120 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 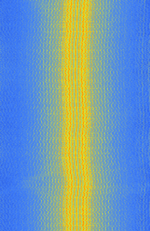 |
|
| Vaisala RS92-KL Weather Balloon (Radiosonde) | RS92-KL and RS92-K are analog radiosondes built by Vaisala in Finland. These radiosondes are used for weather balloons. | 400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 406 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 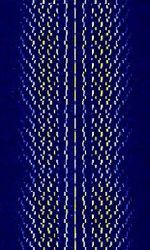 |
|
| Voice Inversion Scrambling | Analog Voice Inversion Scrambling divides the spectra into multiple bands and swaps them. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 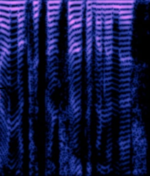 |
|
| WEFAX | Radiofax (Also known as Weatherfax, HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz)-FAX, WEFAX, and Weather Facsimile) is a slow scan analog image transmission mode used for the transmission of weather charts and meteorological reports. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMFrequency Modulation | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 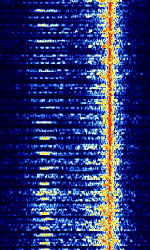 |
|
| Wettersonde E084 (Radiosonde) | The E084 is a radiosonde designed in 1990 by Deutsche Wetterdienst. It broadcasts a temperature reading at 403.05 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz via a FMFrequency Modulation-modulated tone which changes pitch depending on the temperature. | 403.05 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 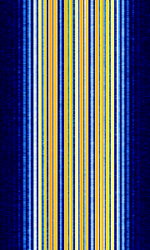 |
|
| Yachta T-219 Voice Scrambler | Yachta or Yakhta (Russian for 'Boat') T-219 is an analogue voice scrambler. It is unique in that an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying sync signal is transmitted in the middle of the main signal, with the scrambled voice stream split above and below the FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 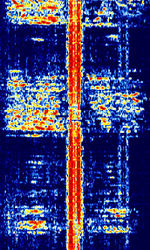 |
|
| ZVEI Selcall | ZVEI is a family of selcall modes defined by the Zentralverband der Electrotechnischen Industrie in Germany. Selcall modes include ZVEI-1, ZVEI-2, ZVEI-3, PZVEI, DZVEI, PDZVEI and ZVEI-VDEW. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
Pages in category "Analogue"
The following 62 pages are in this category, out of 62 total.