ATSC Broadcast
| Broadcast | |
|---|---|
| Analogue Radio: AM radio - FM radio Digital Radio: DRM - DAB |
Description[edit]
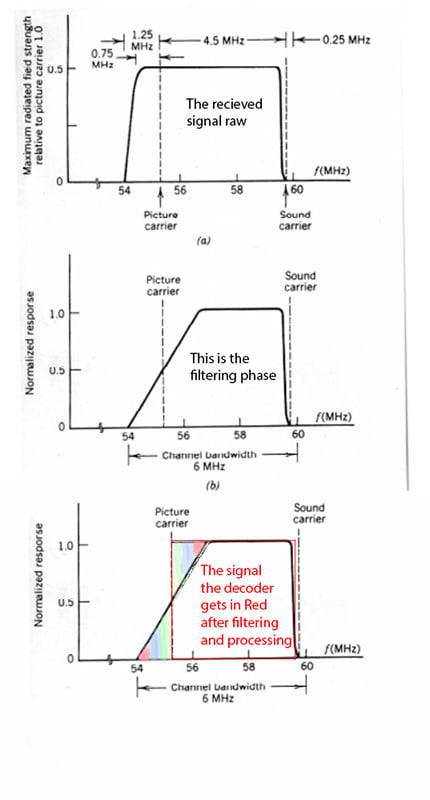
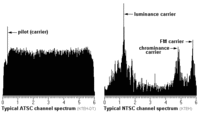
Advanced Television Systems Committee Television. 8VSB Modulation. 8VSB Modulation is a special kind of PAMPulse Amplitude Modulation Modulation.
Each channel has a single carrier signal on the left of the signal.
8VSB[edit]
Vestigal Side Band[edit]
8-Amplitude Keying[edit]
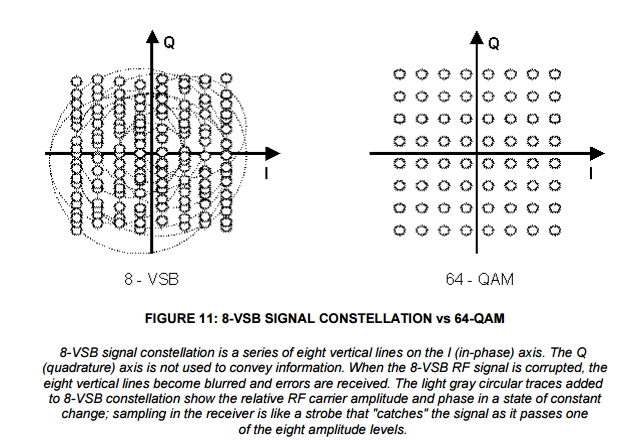
8VSB uses digital amplitude modulation with 8 distinct amplitude levels representing 3 digital bits. If this were ordinary double-sideband AMAmplitude Modulation, these levels would appear as 8 dots along the I (real) axis. However, a Q channel component is created by the vestigial sideband (VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation) filtering that removes most of the lower sideband. The lower sideband is reconstructed in the receiver just as it was in analog TV, and this cancels the Q channel component leaving only the 8 dots on the real axis.
In contrast, 64-QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation uses eight distinct I and eight distinct Q amplitudes to encode one of 64 combinations representing 6 bits, i.e., twice as many per symbol as 8VSB. To do this it must transmit two complete sidebands (which are not mirror images of each other).
Frequencies[edit]
Please update this data the repack has moved most UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) DTV stations to Ch 36 and below. CH 37 remains unused for Radio Astronomy. I've been trying to find out what UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) DTV stations have not been moved but the FCC data base is "sub optimal."
Table is taken from Wikipedia ATSC article.
- In 2009, all US TV stations transitioned to the ATSC 8VSB (digital) signal described above. Although FCC rules only require 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz accuracy, the ATSC pilot (carrier) signal is nominally 309 440.559 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). above the lower edge of the channel. In ATSC the audio and video are multiplexed onto a single digital signal and the video and audio carrier frequencies found in earlier NTSC (analog) TV channel tables are no longer applicable.
| Channel | Lower edge | ATSC pilot | Upper edge | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2 | 54 | 54.31 | 60 | ||
| 3 | 60 | 60.31 | 66 | ||
| 4 | 66 | 66.31 | 72 | ||
| (72-76 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz assigned to other services) | |||||
| 5 | 76 | 76.31 | 82 | ||
| 6 | 82 | 82.31 | 88 | ||
| Channel | Lower edge | ATSC pilot | Upper edge |
|---|---|---|---|
| 7 | 174 | 174.31 | 180 |
| 8 | 180 | 180.31 | 186 |
| 9 | 186 | 186.31 | 192 |
| 10 | 192 | 192.31 | 198 |
| 11 | 198 | 198.31 | 204 |
| 12 | 204 | 204.31 | 210 |
| 13 | 210 | 210.31 | 216 |
| Channel | Lower edge | ATSC pilot | Upper edge |
|---|---|---|---|
| 14 | 470 | 470.31 | 476 |
| 15 | 476 | 476.31 | 482 |
| 16 | 482 | 482.31 | 488 |
| 17 | 488 | 488.31 | 494 |
| 18 | 494 | 494.31 | 500 |
| 19 | 500 | 500.31 | 506 |
| 20 | 506 | 506.31 | 512 |
| 21 | 512 | 512.31 | 518 |
| 22 | 518 | 518.31 | 524 |
| 23 | 524 | 524.31 | 530 |
| 24 | 530 | 530.31 | 536 |
| 25 | 536 | 536.31 | 542 |
| 26 | 542 | 542.31 | 548 |
| 27 | 548 | 548.31 | 554 |
| 28 | 554 | 554.31 | 560 |
| 29 | 560 | 560.31 | 566 |
| 30 | 566 | 566.31 | 572 |
| 31 | 572 | 572.31 | 578 |
| 32 | 578 | 578.31 | 584 |
| 33 | 584 | 584.31 | 590 |
| 34 | 590 | 590.31 | 596 |
| 35 | 596 | 596.31 | 602 |
| 36 | 602 | 602.31 | 608 |
| 37 | 608 | 608.31 | 614 |
| 38 | 614 | 614.31 | 620 |
| 39 | 620 | 620.31 | 626 |
| 40 | 626 | 626.31 | 632 |
| 41 | 632 | 632.31 | 638 |
| 42 | 638 | 638.31 | 644 |
| 43 | 644 | 644.31 | 650 |
| 44 | 650 | 650.31 | 656 |
| 45 | 656 | 656.31 | 662 |
| 46 | 662 | 662.31 | 668 |
| 47 | 668 | 668.31 | 674 |
| 48 | 674 | 674.31 | 680 |
| 49 | 680 | 680.31 | 686 |
| 50 | 686 | 686.31 | 692 |
| 51 | 692 | 692.31 | 698 |
Channel 37 is reserved for the radio astronomy service and no new broadcast stations are assigned to channel 51 to minimize interference to new digital services operating in former UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) TV channel 52.
Decoding Tutorials[edit]
Video Examples[edit]
- 8-VSB in Broadcasting
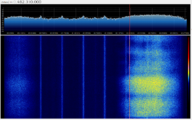
- ATSC RF spectrum waterfall (one channel)
- ATSC RF spectrum waterfall (three channels)