Military
From Signal Identification Wiki
Description[edit]
These are signals that are operated by or are associated with military operations and agencies around the world. Examples include Over the Horizon Radars, STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). data links, military modem and transceiver modes, encrypted radio teletype and encrypted voice.
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 'Ghadir' OTH Radar | 'Ghadir', is an Iranian over the horizon radar, part of Iran's Sepehr Phased Radar System. | 28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 29.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | Pulse | 60 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Iran | 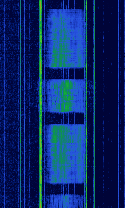 |
|
| 'OTH-SW' OTH Radar | OTHOver The Horizon (very long range)-SW is a Chinese over-the-horizon radar. It is known to operate with pulse repetition frequencies of 43 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). and 86 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).. | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 40 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 80 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 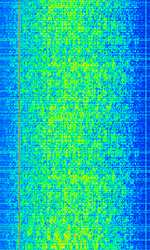 |
|
| 17067bps FSK | Unknown military-use signal reminiscent of SECURENET CVSD voice. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 88 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 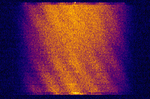 |
|
| 29B6 'Kontayner' OTH Radar | 29B6, nicknamed 'Контейнер' (Kontayner), is a Russian over the horizon radar. It is currently very active in Europe. The radar uses 150 antenna masts with data transmission systems, transmitters and receivers, a power station, and control buildings. It can detect high-altitude and low-altitude aircraft and missiles at very long ranges. | 6.1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 32 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMOP, Pulsed | 3.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 28 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 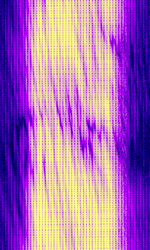 |
|
| 77Ya6 'Voronezh' radar | Voronezh (Воронеж) is a Russian radar family capable of aircraft and ballistic missile monitoring. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 440 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | FMCW | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Russia |  |
|
| AKKORD-SS-PD | Akkord-SS-PD (АККОРД-СС-ПД), also known as “Akkord-165” is a Russian datalink used during the invasion of Ukraine. Akkord is a rather old family of datalink protocols, Akkord-165 being the most recent version. | 7.051 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 1.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 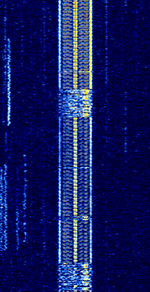 |
|
| ARQ-E(E3) | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-E, also known as ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-1000 Duplex or ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-1000D, is a synchronous full-duplex ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query system. ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-E3 is a variant that uses a different alphabet encoding. Mainly used by French Military Forces. Stations commonly idled for hours on end. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 850 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 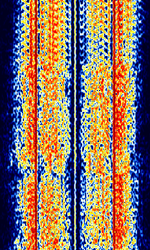 |
|
| ARQ-N | ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-N is a synchronous dual channel ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query mode identical to ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-E, with the only difference being that ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query-N has no symbol inversions. Formerly used by Italian Diplomatic services. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 850 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 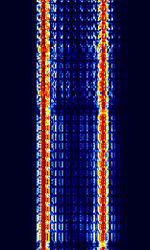 |
|
| Automatic Link Establishment (2G ALE) | Automatic Link Establishment, 2G ALEAutomatic Link Establishment (Official designation MIL-STD-188-141A and/or MIL-STD-188-141B (Appendix A)) is the current standardized method of establishing connections between radio operators. Also known as FED-STD 1045, FED-STD 1049, and STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 5066. | 3.068 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28.313 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 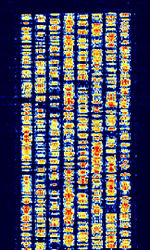 |
|
| Automatic Link Establishment (3G ALE ARCS) | 3G ALEAutomatic Link Establishment (ARCSAutomatic Radio Control System) is the next generation of ALEAutomatic Link Establishment (Designated by MIL-STD-188-141B (Appendix C)). Also known as STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4538, although MIL 188-141 does not provide Fast LSU. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 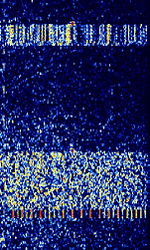 |
|
| BR-6028 | BR-6028 is a VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy (Voice Frequency Telegraph) frequency and time diversity modem using 7 data channels. It is sometimes also known as BARRIE, USA-7, or 6028. | 5.75 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 15.937 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 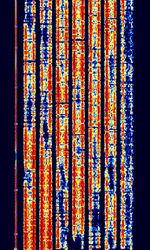 |
|
| CIS 3x100 VFT | Three CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-14 signals overlaid on top of each other in a 3100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy bandwidth, operating at 100 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia |  |
|
| CIS 3x144 VFT | Three 144 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signals in a 3100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy bandwidth. Reportedly phased out. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 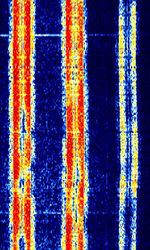 |
|
| CIS 3xBaudot-50 VFT | Three 50 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. Baudot signals in a 3100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy bandwidth. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 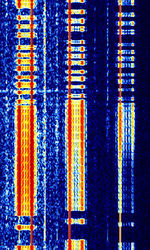 |
|
| CIS FTM-4 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic FTM-4 is the unofficial designation of a four-tone MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying data mode which is apparently used by Russian military. | 4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 13 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 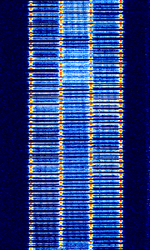 |
|
| CIS MFSK-16 XPB | Enigma designation XPB is a custom 16-tone MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying mode said to have origin from Russian Intelligence and Foreign Ministry stations. | 4.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 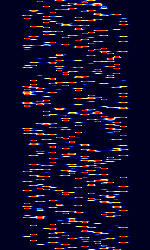 |
|
| CIS MFSK-21-13 | An MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying data mode that is believed to originate from Russian sources. Changes between MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-21, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-13 and different speeds. | 4.834 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 16.292 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 3.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia, Worldwide | 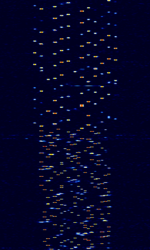 |
|
| CIS MFSK-68 | New Russian MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying Modem that uses 68 MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying (5 tones at a time) as well as a 9000 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. 8-PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol) insert every second which spans 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz wide. This signal is often found attributed with CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-3000, where CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-3000 acts as the ALEAutomatic Link Establishment for this signal as well as CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-128. It is used by Russian diplomatic services and known with the unofficial name "Perelivt". | 7.659 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18.28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 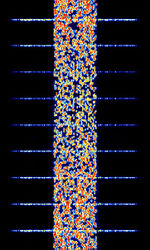 |
|
| CIS OFDM HDR Modem | Russian OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing HDR (High Data Rate) Modem. Has three main modes: CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-45, CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-60, and CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-93, corresponding to the number of OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing tones in the signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 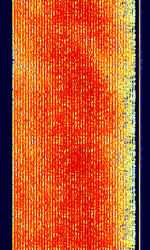 |
|
| CIS-112 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-112 OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing signal. Has a preamble of 7 Tones (not including carrier), then 56 tones before entering into the 112 tone data transmission. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 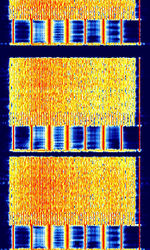 |
|
| CIS-12 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-12 (Also known as MS5, FIRE, AT-3004D, AT-3104D, T-230) is a 12-tone PSKPhase-Shift Keying Russian military multi-channel modem. | 300 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 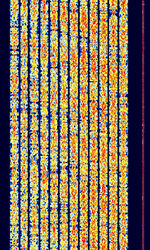 |
|
| CIS-1200 (T-230-1A 'Mahovik') | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-1200, Mahovik, "Flywheel" in Russian, is a PSKPhase-Shift Keying based mode that can transmit both voice and data. It is transmitted from a Russian T-230-1A. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | SDPSK, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 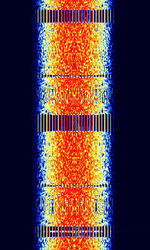 |
|
| CIS-128 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-128 is an OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing mode that uses 128 channels, with one “off” channel in the center, so the signal is divided into two 64 channel parts. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 6.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 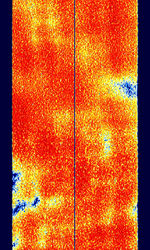 |
|
| CIS-1280 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-1280 is a OQPSK (Offset Quadrature Phase Shift-Keying) modulation data modem signal. Also known as Soviet Mil(MOD)/FAPSIFederal Agency of Government Communications and Information (Russian Agency)/PTTPush To TalkPress to TransmitMinistries of Postal, Telephone, and Telegraph Service (Soviet Agency) system. These stations are recognizable in that they are all placed on .081 offsets from a kilohertz or half kilohertz point. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 13.369 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.28 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 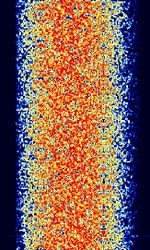 |
|
| CIS-14 | Also known as AMOR and AMOR96. Synchronous FSKFrequency-Shift Keying duplex teleprinter system with ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 650 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 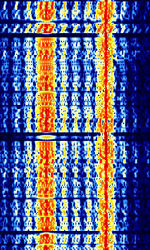 |
|
| CIS-16 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-16 is a BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) 16-tone mode, possibly transmitted from a modified AT-3004D or AT-3104 type Russian military transceiver. Also known as CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic 16x75 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. for the 75 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. speed in each of the 16 sub channels. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 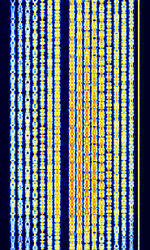 |
|
| CIS-20 | Russian AT-3104 Modem signal, 20-tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing DQPSKDifferential Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying signal. Has characteristic pilot tone located 3300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). from suppressed carrier. All 20 channels operate at 75 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 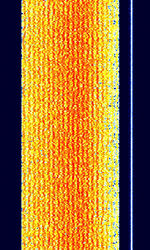 |
|
| CIS-300 | Known as CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-300 Burst, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode used with 300 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. rate with a starting and ending tone on the upper part of the signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 370 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 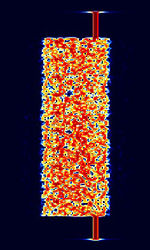 |
|
| CIS-3000 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-3000 is an 8-PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol) Data Modem protocol. Its source is traced to Russia. 3000 is for its 3000 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. speed (maximum speed is technically 9000 bpsBits per second (bps)). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 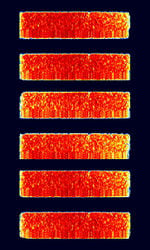 |
|
| CIS-36-50 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-36-50, also known as BEE-36, is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying modem used by the Russian Navy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 550 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 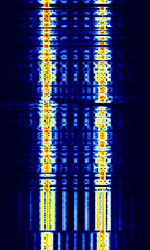 |
|
| CIS-40.5 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-40.5 (Also known as T-206) is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signal used in Russian Military Communications Equipment. Used as a telegraph channel, encrypted. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 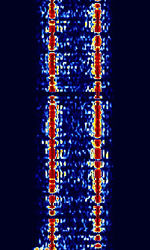 |
|
| CIS-48 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-48 is an interesting data mode with a unique format. It uses a 4 DBPSK Preamble with a constant tone and changing OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing modes as it transmits data. Origin is suspected to be in Russia. | 5.017 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 17.289 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Russia | 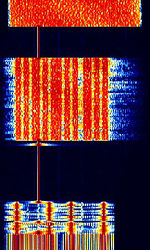 |
|
| CIS-50-50 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-50-50 is very similar to CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-36-50. The main difference is in the available baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. rates and frequency shifts used. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 150 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 630 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 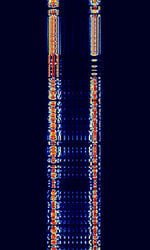 |
|
| CIS-8181 | CISCommonwealth of Independent States (CIS), the former Soviet Republic-8181 is an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying modem used by the Russian navy. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 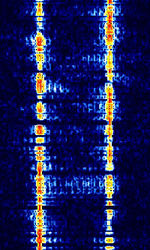 |
|
| CORIOLIS Tactical Direct Broadcast | Direct Broadcast digital signal from the CORIOLIS satellite, primarily carries data from the WindSat instrument. | 2,221.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| CV-786 | CV-786 is a wideband FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode built in Rockwell-Collins MDM-2001 modems. Also known as TRC-75, as it was used in TRC-75 transceivers. A military-based Radio TeleTYpe mode. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 900 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 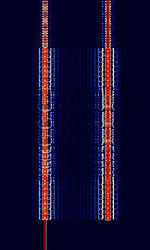 |
|
| Chinese 'Foghorn' OTH radar | A Chinese over the horizon radar, known as "foghorn" among amateur radio operators. Not much is known about it. | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 29 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China, Worldwide | 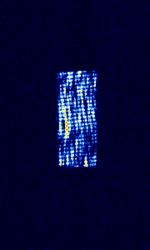 |
|
| Chinese 30-tone OFDM modem | A 30-tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing data mode, probably used by Chinese military or other agencies. | 3.618 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18.656 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | LSBLower Side Band Modulation, USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China, Worldwide | 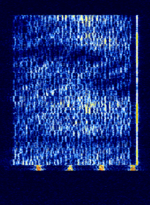 |
|
| Chinese-64 MFSK | Chinese Modem MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying-64 | 3.673 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 16.989 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables),LSBLower Side Band Modulation (rare) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 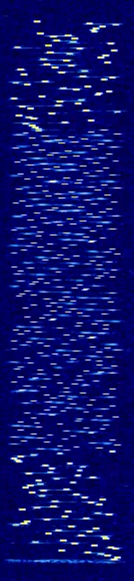 |
|
| Cobra Dane | The AN/FPS-108 COBRA DANE is a PESA phased array radar installation operated by Raytheon for the United States Space Force (originally for the United States Air Force) at Eareckson Air Station on the island of Shemya, Aleutian Islands, Alaska. | 1,215 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | United States | — |  |
|||
| Coquelet | Coquelet is an MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying system, similar to Piccolo. Also known as COQ-8, COQ-12, and COQUELET 8 V 2. Uses ITA-2 charset. It's two main modes are Coquelet-8 and Coquelet-13. No longer in use. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 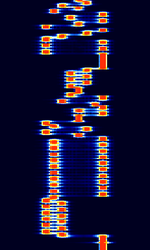 |
|
| Duga radar | Duga (Russian: Дуга́) Soviet over-the-horizon radar, now defunct | 7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 19 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | PM | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 40 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 800 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Chernihiv/Chernobyl, Ukraine; Komsomolsk-on-Amur, Russia | 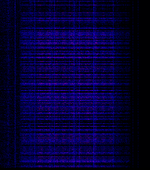 |
|
| F07 number station | F07 is a Russian digital number station known for using multiple modulation types, including MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) and FSKFrequency-Shift Keying. | 5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 17.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 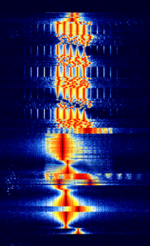 |
|
| GM2100 (R&S) | This is the proprietary HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Data Signal Protocol for the Rohde & Schwarz HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Modem GM2100. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 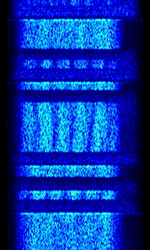 |
|
| GRAVES | The Grand Réseau Adapté à la Veille Spatiale (GRAVES) system is a French space-surveillance system for low-orbit (up to 1000km) satellites. Emitter is based near Dijon, France. | 143.05 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW I/Q | 1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | France | 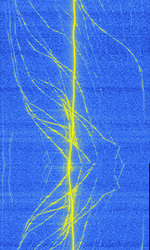 |
||
| GYN2 GBR | Transmitting site owned by the Ministry of Defense. Originally constructed in 1946 and was originally used as a shortwave radio station. In present time, the transmitting site is used by the British Navy in order to transmit encrypted messages to submarines at sea. The site is also capable of DRM and is beamed at 121°, towards Germany and Central Europe | 81 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United Kingdom | 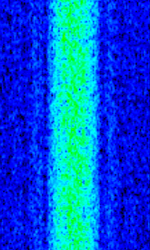 |
||||
| HC-265 Voice Scrambler | HC-265 is a Voice Scrambling mode developed by Hagelin Crypto for their HC-265 CRYPTOCOM secure voice unit. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 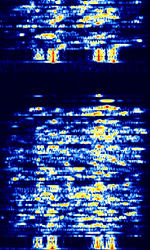 |
|
| HFGCS (High Frequency Global Communications System) | HFGCS is a series of networks deployed by the United States Air Force to send encoded messages to deployed aircraft. This network is well known for it's coded EAM's (Emergency Action Messages) used for coordinating United States Strategic Nuclear Forces. | 4.724 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 15.016 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.95 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 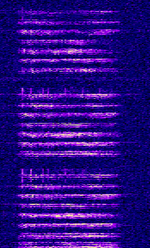 |
|
| High Frequency Data and Voice Link (HFDVL) | HFDVL (or HFD+VL) is an experimental mode developed by research groups from The University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria and The Polytechnic University of Madrid. This mode is intended for military use in accordance with STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 5066 parameters. | 14.35 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 14.829 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Spain | 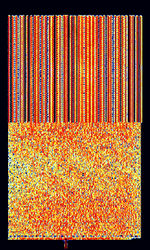 |
|
| ICV | ICV is a NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization-operated VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) transmitted located in the island of Tavolara, Sardinia, Italy. | 20.27 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 20.76 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Italy | 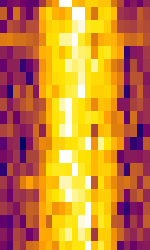 |
||
| Iranian Navy QPSK Modem | Iranian Navy QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) Modem is a QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) mode used by the Iranian Navy. It has gone through several versions. The current version (2015) is V2 and supports speeds of 468 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 936 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., and 1872 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.. | 8.046 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 17.382 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2.85 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Iran | 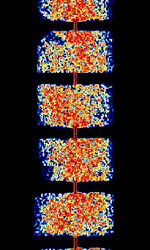 |
|
| Israeli Navy Hybrid Modem (188-110 MOD) | The Israeli Naval Hybrid Modem is based on the MIL-STD-188-110 Serial Standard. Has characteristic preamble with 4/6 Tone and 18 QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) parallel mode before 110 Serial transmission. Possible use as a broadcast transmitter for ships. Used by the Israeli Navy 4XZ station from Haifa. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Israel | 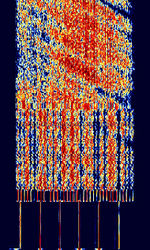 |
|
| Israeli VFT | Israeli based VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy transmission, most likely used by Israeli government or military. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Israel | 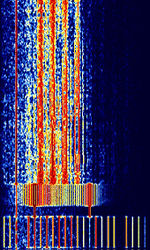 |
|
| Japan Military 8-Channel FSK | Data signal thought to originate from Japanese Military/Navy | 4.295 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 16.554 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Japan | 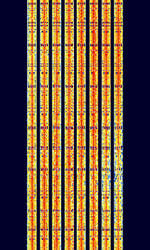 |
|
| Japanese Slot Machine (XSL) | The Japanese Slot Machine (Enigma Designation XSL) is a simplex system used by the Japanese Maritime Self-Defense Force in Ichihara, Japan. | 4.153 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8.703 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Japan | 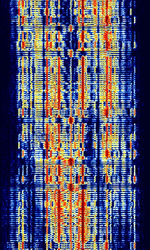 |
|
| Jim Creek (NLK) | Jim Creek Naval Radio Station is used by the US Navy to transmit commands to distant submarines. | 24.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 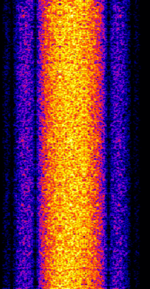 |
|
| Jindalee Operational Radar Network (JORN) | JORN is an Australian OTHR system that operates uniquely in that it's radar bursts include an intro tone before the burst. | 5.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 33 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 60 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Australia | 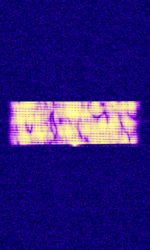 |
|
| Link-11 | Link-11 (Also known as ALLIGATOR, STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 5511, TADIL-A, MIL-STD-6011, and MIL-STD-188-203-1A) is a Tactical Data Link standard (formerly known as Tactical Digital Information Link (TADIL) used by NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization and the US Military for Maritime Tactical Data Exchange. | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 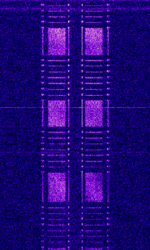 |
|
| Link-11 (UHF) | This is the UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) band variant of Link-11, which is transmitted on a FMFrequency Modulation carrier. The FMFrequency Modulation-demodulated baseband is identical to the HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Link-11 waveform. | 225 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 399.975 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 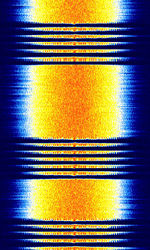 |
|
| MD-522 | MD-522 (Also known as MIL-M-55529A) is a synchronous FSKFrequency-Shift Keying mode built into GRC-MD522 teletypewriter sets and used for wirelessly transmitting ASCII information. MD-522 has a narrowband, wideband, and diversity mode. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 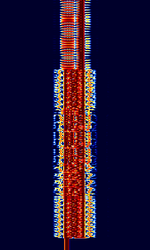 |
|
| MD-674 | MD-674, also known as Wireline FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, is a very old United States Military FSKFrequency-Shift Keying Modem from the 1960's. Uses 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). FSKFrequency-Shift Keying shift. Speeds of 50 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 75 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., 100 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., and 150 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. have been logged. No longer seen today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States |  |
|
| MIL-STD-110-342 | MIL-STD-110-342 was a US Dept. of Defense standard for a 16 channel VFTVoice Frequency Telegraphy teletype transmission. This mode was officially cancelled as of December 5th, 1995. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 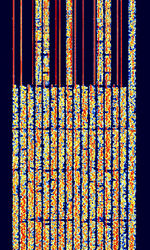 |
|
| MIL-STD-188-110 Appendix A 16-Tone | MIL-STD-188-110 Appendix A is a 16-tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing PSKPhase-Shift Keying signal used to transmit data. As of 110C revision, this mode is being phased out. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 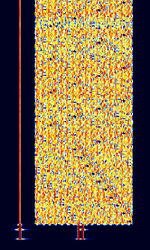 |
|
| MIL-STD-188-110 Appendix B 39-Tone | MIL-STD-188-110 Appendix B is a 39-tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing DQPSKDifferential Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying mode used to send data and voice. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 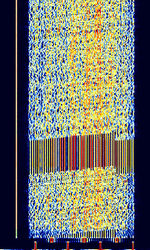 |
|
| MIL-STD-188-110 Serial | MIL-STD-188-110 Serial is a US Department of Defense standard for HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Communications, Serial PSKPhase-Shift Keying mode. Can transmit both data and voice with a range of interleaving and speed modes for optimal propagation. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 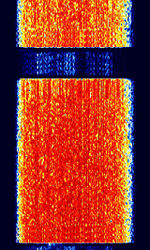 |
|
| Marconi Selenia 25-Tone Modem | The Marconi Selenia 25-Tone Modem is a military modem developed sometime around 2003 by Marconi Selenia Communications (Now Finmeccanica). It supports ECCMElectronic Counter-CounterMeasures (ECCM) is a part of electronic warfare which includes a variety of practices which attempt to reduce or eliminate the effect of electronic countermeasures (ECM) such as jamming. ECCM is also known as electronic protective measures (EPM), chiefly in Europe. capability and transmits at a datarate of 2400bps. This mode was employed by Turkey. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 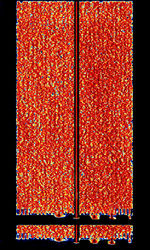 |
|
| Milstar | UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) FHSS Downlink of Milstar, a US joint military service satellite communications system that provides secure, jam resistant, worldwide communications. Nicknamed 'Waterdroplets' for it's characteristic waveform and sound. | 243.785 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 243.822 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | FHSS | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Modernised High Frequency Communications System (MHFCS) | The Modernised High Frequency Communications System (MHFCS) is an Australian Department of Defense HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) System for their military communications network. Also known as AUS MIL ISBIndependent Side Band Modulation Modem, AUS MHFCS, and ADF HFCS. | 2.01 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 27.478 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 750 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Australia | 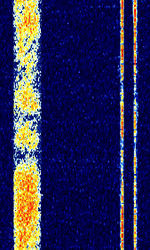 |
|
| Monaco Enterprises MAAP Fire Alarm | Fire alarm control panel built for the United States of America's Department of Defense. | 138.95 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 139.675 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States |  |
|
| Morse Code (CW) | CWContinuous Wave Morse Code is the simplest form of transmission found virtually all over the RFRadio Frequency bands for a variety of uses. The most common use of this is for Call-sign Beacons by both Amateur and Military operators. | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 250,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | Worldwide |  |
||
| NML | Naval Radio Transmitter Facility (NRTF) transmits encrypted commands to submerged US submarines. | 25.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 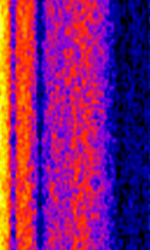 |
|
| NOV | TACAMO (take charge and move out) is the back up communications system to the US nuclear submarine fleet in case an attack on land based transmitters disables them. A rotating fleet of Navy E6 jets equipped with 200 KW transmitters and two 2½-mile-long trailing wire antennas (TWA) at 35,000 ft altitude to provide 24/7 coverage. Short pings are transmitted every few seconds. | 26.9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | Worldwide | 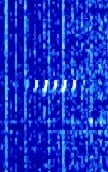 |
|||
| NPM | Naval Radio Transmitting Facility (NRTF) sends encrypted commands to submerged US naval submarines in the Pacific. | 21.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United States | 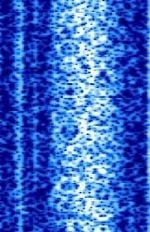 |
|
| NWC | Naval Communication Station (NCS) Harold E. Holt. Used jointly by the Australian and United States navies to transmit encrypted orders to submerged submarines in the Pacific. | 19.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Australia | 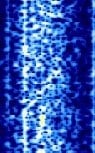 |
|
| One Beep, Two Beeps | One Beep, Two Beeps is a nickname given to a signal emitted by the Norwegian Navy communications center in Bodø | 4.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 6.429 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | Norway | 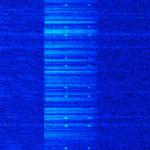 |
|||
| PLUTO II OTH Radar | PLUTO II is an Over The Horizon Radar located in the Sovereign Base Area just outside RAF Akrotiri in Cyprus. PLUTO II is very active in Europe. | 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 38 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 40 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Cyprus | 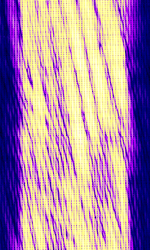 |
|
| PRC-16 | PRC-16 is a Chinese sourced PSKPhase-Shift Keying data link, traced to Shanghai. Suspected user Chinese Military. | 14.3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 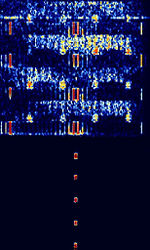 |
|
| Panther-H Modem | Panther-H is an intelligent frequency hopping transceiver developed by Racal (now Thales Group). Has a signature 8-burst SOC (Start Of Conversation) sync procedure. Used in Panther-2000H radios | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 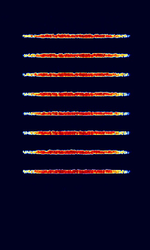 |
|
| Piccolo | Piccolo was a MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying system developed by the UK Foreign and Commonwealth Office (FCO) to communicate with foreign embassies and UK military stations around the world. No longer used. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 180 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 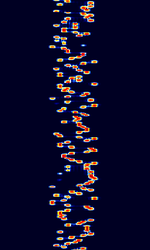 |
|
| Podsolnukh 'Sunflower' Radar | A Russian over the horizon radar, also known as "Sunflower" | 3.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis. | FMOP | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia, Worldwide |  |
|
| Q-MAC HF Modem | The Q-MAC HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Modem is a military modem developed by Q-MAC (acquired by Barrett Communications). It uses OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing with a BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) sync channel in a gap of the signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, PSK8 | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 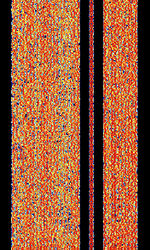 |
|
| RDL VLF | RDL is a Russian VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) station located in Krasnodar. It is one of the few VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) stations that changes modes during routine transmissions. | 18.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 27.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, CWContinuous Wave-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia | 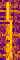 |
|
| Radioteknicheskaya Systema Dalney Navigatsii (RSDN-20) | RSDN-20, also known as Alpha, is a Russian hyperbolic radio navigation system. Presumed to be used for Russian ships, submarines and aircraft in the northern hemisphere, possibly worldwide. | 11.91 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 14.88 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | CWContinuous Wave | 20 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Russia |  |
||
| Relocatable Over-the-Horizon Radar (ROTHR) | Relocatable Over-the-Horizon Radar (ROTHR), also known as AN/TPS-71, is an OTHOver The Horizon (very long range) Radar used by the United States Navy that uses bistatic ionospheric backscattering for wide area surveillance. | 5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 28 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FMCW | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 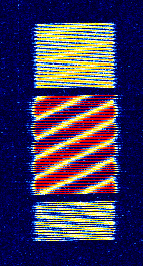 |
|
| Russian MFSK-OFDM-chirp hybrid modem | A supposedly Russian HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) data mode with MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing and frequency sweeps, resulting in an interesting spectrogram and sound. | 12.176 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 16.259 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, FMFrequency Modulation, FMCW | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 96 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia, Worldwide | 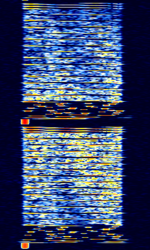 |
|
| Russian military 20bd 7kHz FSK | Slow 20-baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signal with very large 7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz frequency shift. Used by Russian military. | 7.041 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 7.063 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 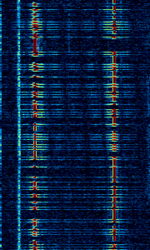 |
|
| S-Band Jammer | This is what the signal of a military S-Band (In this case 2.4 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz) RADAR and WiFi intentional interference (Jamming) device looks like. This signal is generated by a DDS system and is then used to modulate the output of a 2.45 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz magnetron (The same as in a microwave oven). | 2,400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Noise | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 100 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
|
| SAS/SRC | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio) | 40.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 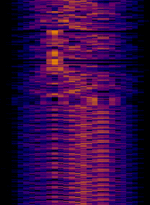 |
|||
| SAS2 | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio) and is activated less often as the other Swedish transmitters used for VLFVery Low Frequency (3-30 kHz) submarine communication. Usually, it works with reduced power. | 42.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 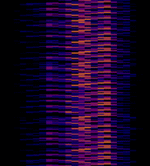 |
|||
| SAS3 | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio). | 44.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 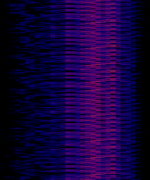 |
|||
| SECOR 4 (EGRS 4) | SECOR 4 (COSPAR ID: 1965-027B) was a SEquential COllation of Range series satellite, and is occasionally active when receiving adequate solar power on it's panels. It is not consistent, likely owing to a tumbling or rotating motion. | 136.845 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | IRIG | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz |  |
||
| SHR | Swedish navy transmitter for submarine communication. It shares the antenna with SAQ (Grimeton Radio). | 38 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | Sweden | 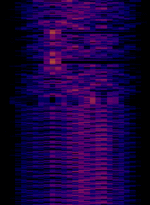 |
|||
| STANAG 4197 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4197 is a NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing signal used in ANDVT modems that transmit encrypted digital voice over HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 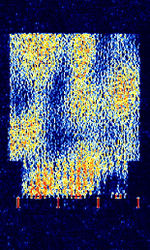 |
|
| STANAG 4285 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4285 is specified by the NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) Military Agency for Standardization in "Characteristics of 1200 / 2400 / 3600 Bits per Second Single Tone Modulators / Demodulators for HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Radio Links" | 1.89 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 22.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 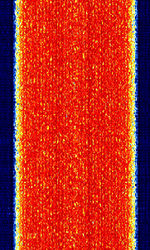 |
|
| STANAG 4415 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4415 is a NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization standard for robust, non-hopping digital data communication, used on severely degraded HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) channels with large Doppler and multipath spreads. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 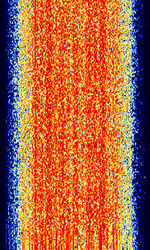 |
|
| STANAG 4481 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4481, also known as CRATT, Link-4, and NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization-75, is specified by the NATONorth Atlantic Treaty Organization (North Atlantic Treaty Organization) Military Agency for Standardization as a "Minimum technical equipment standards for naval HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) shore-to-ship broadcast system" | 2.815 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18.016 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 1.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.75 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 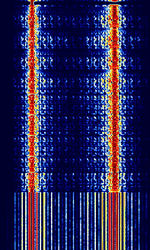 |
|
| STANAG 4529 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4529 a modification of STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4285 to deliver data and voice in 1240 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). of bandwidth at rates of up to 1800 bpsBits per second (bps). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), 8PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol) | 1.24 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 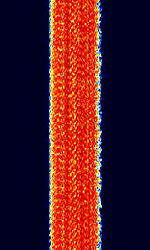 |
|
| STANAG 4539 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 4539 or MIL-STD-188-110B/C Appendix C is a HDR (110B) / MDR (110C) serial PSKPhase-Shift Keying/QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation signal that can reach speeds up to 9600 bpsBits per second (bps) (12800 bpsBits per second (bps) with no interleaving). | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 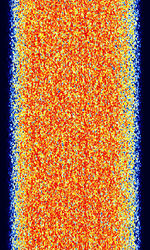 |
|
| STANAG 5065 | STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). 5065 is defined as "Minimum Standards for Naval Low Frequency (LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz)) Shore-To-Ship Surface Broadcast Systems", with two primary protocols, FSK75 and MSK300. | 50 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 160 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, MSKMinimum-Shift Keying (When Shift/Bd = 0.5. It is impossible to get this ratio to be lower than 0.5, hence it is called the 'Minimum' shift.) | 235 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 360 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Saab Grintek MHF-50 MFSK Modem | The MHF-50 MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying Modem by Saab Grintek Technologies in South Africa is a data modem that utilizes RTTYRadio TeleTYpe, 2-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, and 33-MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying to transmit data | 4.245 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 12.982 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | South Africa |  |
|
| Siemens CHX-200 FSK Modem | CHX200, also known as Siemens CHP200 and PRC-921/GY, is a backpack HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) ECCOM transceiver, designed and built by Siemens. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| SkyOFDM | Data transmission mode developed by SkySweep Technologies in Finland. Probably used by Finnish MFA | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Finland | 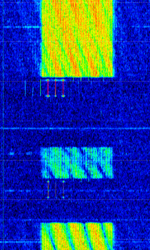 |
|
| Tactical Air Navigation System (TACAN) | Radio navigation technology that measures the slant range (distance) between an aircraft and a ground station by timing the propagation delay of radio signals. | 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,213 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | PAMPulse Amplitude Modulation | Worldwide | 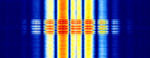 |
|||
| Thales SALAMANDRE (HFXL) | Thales SALAMANDRE (using HFXL waveform) uses up to 16 separate contiguous or not-contiguous narrowband HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) channels for high datarate military and tactical communications. Operates on a modified STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).-4539 platform. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 150 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 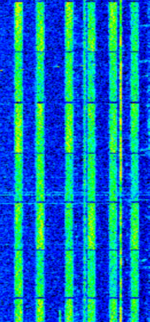 |
|
| Thales Système 3000 HF Modem | Thales Système 3000 is a HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) modem capable of many different modes of transmission. It has a unique preamble and format to it's signals. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 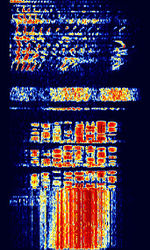 |
|
| Thales Système 3000 Skyhopper | Thales Système 3000 Skyhopper is the frequency hopping mode of the Système 3000 Modem. Characterized by it's very short bursts and frequency hopping behavior. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 2.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 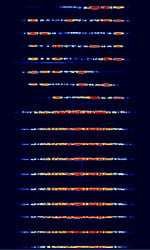 |
|
| Thales Système 3000 Voice Scrambler | Voice Scrambling mode from Thales Système 3000 HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Modem. Has characteristic PSKPhase-Shift Keying and MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying bursts at the beginning and end of a voice transmission. | 1.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| The 'Air Horn' | "The Air Horn" is a Russian military commandment network serving the Western Military District, which also serves the same purpose as the buzzer. It was first heard in 2017, broadcasting on 4020 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz. 2 years later, in 2019, it changed to broadcast instead on 4070 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz (for about 2 months). A few months later, it was temporarily active on 3510 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz, before moving permanently to 3510 in October 2019. In December 2019, the channel marker broke down, and remained inactive until January 2020, broadcasting back on 3510 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz. In September 2022, it moved to 4930 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz, while broadcasting its first known voice messages almost a week after. After December 2023, the channel marker was replaced by The Goose's channel marker. It has not been heard since most likely December 2023 or very early 2024. The stations' last message was broadcasted in July 2023. | 4.93 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Smolensk, Russia | 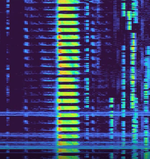 |
||
| The Alarm | Channel marker of a Russian military station nicknamed "The Alarm". "The Alarm" is a Russian military commandment network serving the Western Military District. So far, apart from test counts, it has not been heard with any actual traffic. | 4.77 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 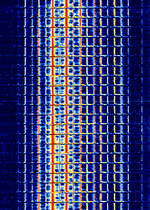 |
||
| The Buzzer (ZhUOZ MDZhB UZB76) | The Buzzer, call-sign NZhTI (formerly ANVF, ZhUOZ, MDZhB and UZB-76), is a Russian Military Commandment system signal used to broadcast diplomatic ciphered messages known as "monolit" to the russian navy. If there is no message to broadcast, its "homing" signal is a loud ship-horn buzzing sound. It is believed to serve a similar purposes to The Alarm and The Air Horn. | 4.625 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | 2.8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 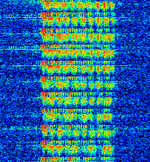 |
|
| The Goose | "The Goose" is a Russian military commandment network serving the Western Military District. It broadcasts on 4310 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz during daytime, changing to 3243 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz for nighttime. | 3.243 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 4.31 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | AMAmplitude Modulation | 3.1 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 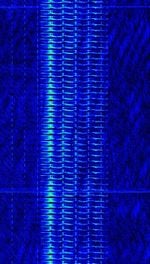 |
|
| The Pip | The Pip is the nickname given by radio listeners to a shortwave radio station that broadcasts on the frequency 5448 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz by day, and 3756 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz during the night. It broadcasts short, repeated beeps at a rate of around 50 per minute, for 24 hours per day. The beep signal is occasionally interrupted by voice messages in Russian. The Pip has been active since around 1986 when its distinctive beeping sound was first recorded by listeners. While its official name or callsign is not known, some of the voice transmissions begin with the code 8S1Shch (Cyrillic: 8С1Щ), which is generally considered to be the name of the station. However, this code may not be a callsign, but instead, serve some other purpose. Radioscanner.ru identifies the owner of this station as a North-Caucasian military district communication center with callsign "Akacia" (ex-72nd communication center, Russian "72 узел связи штаба СКВО") | 3.756 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 5.448 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables),AMAmplitude Modulation | Russia | 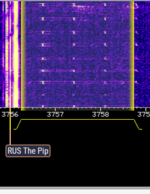 |
|||
| Transit 5B-5 | Transit 5B-5, a former TRANSIT navigation satellite, is the oldest satellite known to still transmit a signal. Considered "dead" because its navigational systems failed after 19 days of operation, it still emits a telemetry signal when illuminated. | 136.658 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | PCM, PAMPulse Amplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation, PM | 32 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 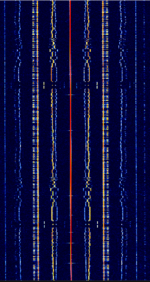 |
|
| UK GOV MIL WINDRM51 | UK GOV/MIL "WinDRM51" variant. Unknown purpose, But link between UK & Cyprus has been found some years ago. | 9.104 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 13.451 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 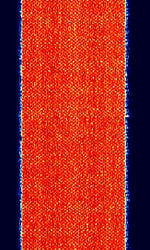 |
|
| VISEL | VISEL, also known as YUG-MIL 120.9 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., FECForward Error Correction-12, and YUG-MIL FECForward Error Correction, is a synchronous teleprinter system used by the former Yugoslav military. No longer active today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Europe | 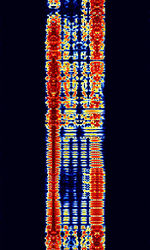 |
|
| XMPP trials | XMPP (Extensible Messaging and Presence Protocol) on shortwave is used by the military and are known for using MIL 188-110A Serial HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) waveform and 6-bit code clear text with dual bursts of STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).-5439 and STANAGNATO Standardization Agreement (STANAG), defines processes, procedures, terms, and conditions for common military or technical procedures or equipment between the member countries of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO).-5066 as for XMPP Multi-User Chat (MUC) messages | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 7.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 34 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 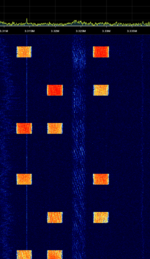 |
|
| Yachta T-219 Voice Scrambler | Yachta or Yakhta (Russian for 'Boat') T-219 is an analogue voice scrambler. It is unique in that an FSKFrequency-Shift Keying sync signal is transmitted in the middle of the main signal, with the scrambled voice stream split above and below the FSKFrequency-Shift Keying signal. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Russia | 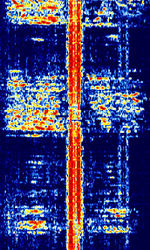 |
|
| Yugoslavian 20-Tone Modem | The Yugoslavian 20-Tone Modem, also known as YUG-MIL 20-Tone and YUG Diplo 20-Tone, is a 20 tone OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing PSKPhase-Shift Keying modem used in former Yugoslavia for military and diplomatic use. No longer used today. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 2.2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 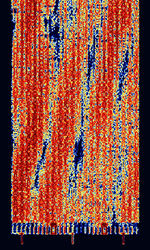 |
|
| Zaliv52 | Military shortwave station broadcasting from the Western Military District in Russia. First heard in March 2017, this station has no channel marker, and it mainly broadcasts Monolith type messages and "MOLNIYA 5X" (МОЛНИЯ 5X) messages addressed to "Zaliv52" (Залив52). | 4.11 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | J3E | Moscow, Russia (speculated) | 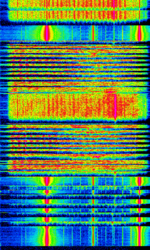 |
Pages in category "Military"
The following 130 pages are in this category, out of 130 total.