Commercial
From Signal Identification Wiki
Description[edit]
These are commercial signals including Paging, Broadcast, Cellular, Satellite, and Land-Mobile Radio.
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1G (NMT) Nordic Mobile Telephone | Nordic Mobile Telephone (NMT, NMT-450, and NMT-900) is a first generation analog cell phone system. Originally designed for and by Nordic countries (Finland, Sweden, Norway, Denmark) it was widely deployed around the world. Nowadays (as of 2015) NMT is defunct. | 453 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 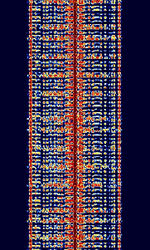 |
|
| 1G Advanced Mobile Phone System (AMPS) | The first generation of cellular mobile telecommunications, which used analogue NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation voice. | 824 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 894 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 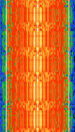 |
|
| 2G (GSM) Global System for Mobile Communications | GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a standard developed by ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards. to describe the protocols for second-generation (2G) digital cellular networks used by mobile phones. As of 2014, it has become the default global standard for mobile communications. | 850 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW, AMAmplitude Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 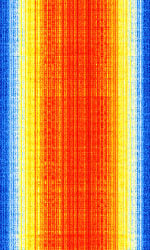 |
|
| 2G CDMA (IS-95) | CDMACode Division Multiple Access-One also known as IS-95, was the first ever cellular standard technology based on Code Division Multiple Access (CDMACode Division Multiple Access). It is a predecessor of the 1xRTT (CDMA2000/IS-2000) standard, which is backwards compatible. | 815 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,995 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | DSSS/QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 1.228 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 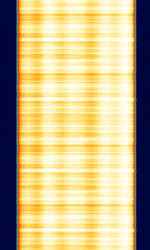 |
|
| 3G WCDMA | WCDMA, known primarily as 3G mobile, is a family of 3G data protocols used to send voice, text and signaling data to smart phones and other wireless devices. | 824 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 2,100 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW, AMAmplitude Modulation | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 4.2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | 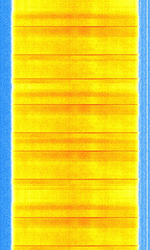 |
||
| 4G (LTE) Long Term Evolution Uplink | Acquired via telecommunications carrier hardware during interference investigation of an Australian cellular network. | 700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3,500 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SC-FDMAFrequency Division Multiple Access | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), 16QAM, 64QAM | 1.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 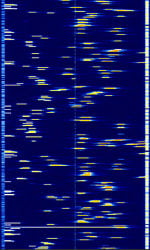 |
|
| 4G LTE Network | Long Term Evolution Network. Also known as 4G LTE Data and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA). Data service for wireless consumer devices. | 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3,500 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM, QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 1.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 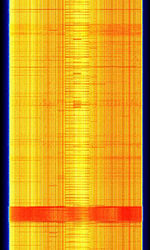 |
|
| 4G LTE450 | LTE 450 refers to the deployment of Long-Term Evolution (LTE) technology in the 380-512 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz frequency band. LTE 450 networks allow various 4G LTE options to deliver efficient and reliable telecommunications services: LTE, LTE-M, and NB-IoTInternet of Things. | 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | OFDMA, SC-FDMAFrequency Division Multiple Access | 1.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 4.74 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| 5G 'New Radio' Cellular Radio - Downlink | 5G cellular, also known by 3GPP '5G' NR (new radio), etc. is a newly released cellular standard that allows for backwards compatibility with 4G LTE, and will allow for several gigabits of connection speeds, (up to 10-100Gb) per second. This is the 600 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz downlink band for the new standard. | 600 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 50,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CP-OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM | 5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 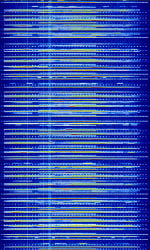 |
|
| 5G (NR) New Radio Uplink | 5G cellular, also known by 3GPP '5G' NR (new radio), etc. is a newly released cellular standard that allows for backwards compatibility with 4G LTE, and will allow for several gigabits of connection speeds, (up to 10-100Gb) per second. This is the 600 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz downlink band for the new standard. | 600 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 50,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CP-OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM | 5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 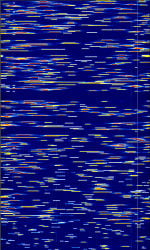 |
|
| 5G Broadcast (MBMS) Multimedia Broadcast / Multicast Service | A technology originally introduced in LTE (eMBMS) that enables efficient transmission of the same content to a large number of users at once — that is, broadcast or multicast instead of individual unicast. In 5G, its evolution is used for the so‑called LTE‑based 5G Terrestrial Broadcast. | 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 694 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), 16QAM, 64QAM | 5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Europe |  |
|
| ASCII | ASCII (also known as ITA5 or IRA) is an amateur radio telegraphy signal using the ITA-5 alphabet. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation, USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 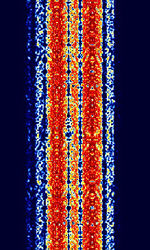 |
|
| ATSC 3.0 Broadcast | The Advanced Television Systems Committee (ATSC) 3.0 standard (marketed as NextGen TV) is a revised set of video broadcasting specifications that outlines improvements to spectrum efficiency. | RAW | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | United States, South Korea, Jamaica | — | 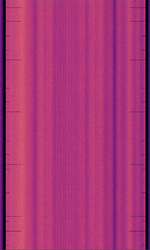 |
|
| ATSC Broadcast | Advanced Television Systems Committee Television. 8VSB Modulation | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | 8VSB | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | United States | — |  |
| Altai Radiotelephone | The initial generation of cellular mobile radiotelecommunications, similar to trunked radio. -- (Audio Sample is *loud*) -- | 300 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 342 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 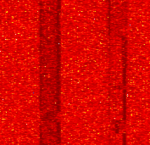 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation (AM) | Long range commercial broadcast and international radio. Also used for aviation communications. | 153 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 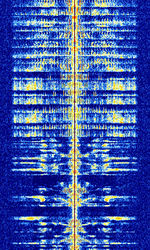 |
|
| Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) | Amplitude Modulation Signalling System (AMSS) is a DRM-based radiotext and data technology for AMAmplitude Modulation broadcasting, like RDS that is used for FMFrequency Modulation. It transmits as a subcarrier, phase-modulating the carrier frequency. | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | 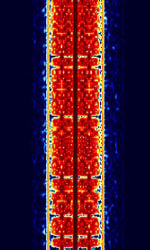 |
||
| Aprizesat | Data downlink from Aprizesat microsatellites. Aprizesat constellation consists of 12 Active satellites, These provide a worldwide M2M asset tracking service and relay AIS packets. | 400.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 400.65 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 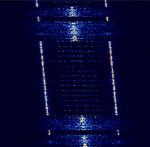 |
|
| Autocab | This is an example of the Autocab Media Data Terminals used by cab companies all over the world. | 163.375 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United Kingdom | 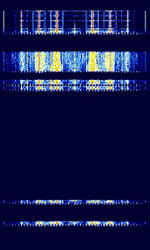 |
|
| B-Netz | B-Netz, was an analog, commercial mobile radio telephone network that was operated by the Deutsche Bundespost in Germany (at first only West Germany) from 1972 until 1994. The system was also implemented in neighboring countries Austria, The Netherlands and Luxembourg. | 148 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 153 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 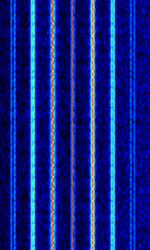 |
|
| Broadband Global Area Network (BGAN) | Proprietary satellite network owned and operated by Inmarsat that provides cellular 3G equivalent data and voice services to subscribers. | 1,525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,559 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 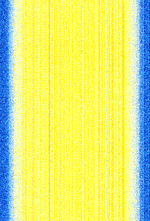 |
|
| CBET | CBET "Critical Band Encoded Tones" are tones added into radio broadcast's audio output for identification purposes. | 520 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation, AMAmplitude Modulation | 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 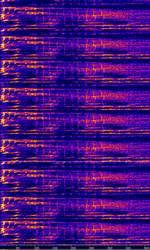 |
|||
| CCIR 493-4 Selcall | CCIRComité Consultatif International pour la Radio (Predecessor of the ITU-R) 493-4 Selcall, also known as HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) Selcall, Australian Selcall, and Codan 8580 Selcall, is a Selcall standard developed in Australia for the HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) band. Used by Amateur radio and Codan Modems. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 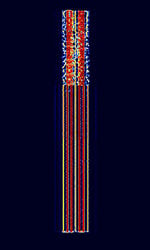 |
|
| CDMA2000 (3G physical layer) | CDMA2000, or IS-2000, is a cellular network standard utilizing the CDMACode Division Multiple Access technology for calls and data. | 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 1.23 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | United States | 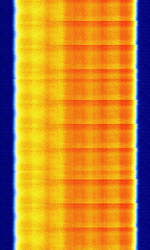 |
|
| CDMA420 | 410 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 425 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 2.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Poland | 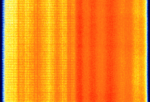 |
||
| China digital radio (CDR) | Convergent Digital Radio (CDR) or China Digital Radio is an in-band-on-channel (IBOCIn-Band On-Channel (IBOC) is a hybrid method of transmitting digital radio and analog radio broadcast signals simultaneously on the same frequency.) digital radio broadcasting format used in China. It can be found in multiple bandwidth configurations with different modulation formats. | 106.1 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 500 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | China | 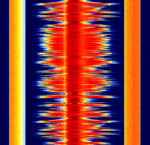 |
|
| Digital Audio Broadcasting (DAB) | DAB is an audio broadcasting standard containing a multiplex of digital radio stations in the signal. | 174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 239 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.536 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | ||
| Digital Audio Broadcasting Plus (DAB+) | DAB+ is a medium of delivering broadcast radio, containing multiple stations in a single multiplex. | 174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 230 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.536 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | |||
| Digital Dispatch Systems MDT | Digital Dispatch Systems Mobile Data Terminal is a dispatching system used by taxi and private transportation companies. | 152 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 854.788 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States |  |
|
| Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications (DECT) | DECT is a ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards. standard for short range communications, mainly cordless phones. It uses a 10 channel/24 slots in a TDMATime Division Multiple Access FDD structure. Audio sample is 100 times slower than real for listening purposes. | 1,880 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 1.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 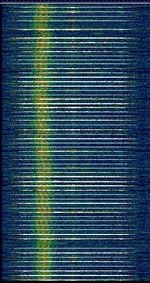 |
|
| Digital Multimedia Broadcasting (DMB) | Digital Multimedia Broadcasting (DMB) is a digital radio transmission technology developed in South Korea as part of the national IT project for sending multimedia such as TV, radio and datacasting to mobile devices such as mobile phones, laptops and GPS navigation systems. | 174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 216 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | DQPSKDifferential Quadrature Phase-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.536 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | South Korea | — |  |
|
| Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) | Digital Radio Mondiale (DRM) is a digital commercial broadcasting mode used to deliver FMFrequency Modulation-comparable sound quality to shortwave radio. | 531 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 26.06 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 4.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 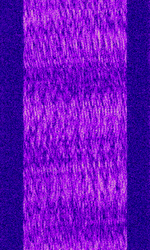 |
|
| Digital Radio Mondiale Plus (DRM+) | DRM+ is a VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) implementation of DRM primarily for the FMFrequency Modulation broadcast band. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 230 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
|
| Digital Video Broadcasting — Cable (DVB-C) | DVB‑C is a cable‑based digital TV transmission standard that delivers MPEG transport streams over coaxial networks using QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation modulation. It was first published as ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards. EN 300 429 and defines the framing, channel coding, and modulation needed for reliable multi‑program distribution via cable. The system uses 16‑QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation up to 256‑QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, allowing high spectral efficiency while maintaining very low error rates thanks to forward error correction. It has become the dominant global standard for digital cable TV outside North America. | 366 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 662 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | 16QAM, 32QAM, 64QAM, 128QAM, 256QAM | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Europe |  |
||
| Digital Video Broadcasting — Satellite (DVB-S) | DVB‑S and DVB‑S2 are both satellite broadcasting standards, but DVB‑S2 is a more advanced and efficient evolution of the original system. | 10,700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 12,700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | ACM/VCM | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), 8PSK8-Phase Phase-Shift Keying (3 bits per symbol), 16APSK, 32APSK | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 72 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Europe, Asia | 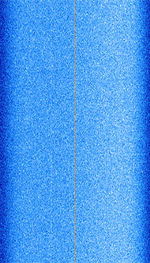 |
|
| Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial (DVB-T) | Digital Video Broadcasting — Terrestrial (DVB-T) is a digital broadcast television format used in Europe and in many other countries in the world. | 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 694 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | COFDMCoded Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 16QAM, 64QAM, 256QAM | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Digital-Coded Squelch (DCS) | Digital in-band signalling used to squelch and manage transmissions on a given frequency. | 433 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 446 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | Worldwide | 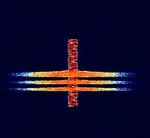 |
||
| European Radio Message System (ERMES) | European Radio Message System (ERMES) is a European common standard for paging developed by the European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ESTI) | 169.413 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 169.833 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 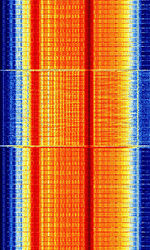 |
|
| FLASH-OFDM | Fast Low-latency Access with Seamless Handoff Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing (FLASH-OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing) is a mobile data access technology developed by Flarion. | 461.31 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 465.73 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | MC-CDMACode Division Multiple Access | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Finland, Slovakia, Germany, United States | 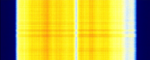 |
|
| FLEX | FLEX (Flexible Wide Area Paging Protocol) is Motorola's high speed one-way paging protocol that supports 1600, 3200, and 6400 bpsBits per second (bps). FLEX can transmit tone, numeric, alphanumeric, and binary data. | 152.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 931.938 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 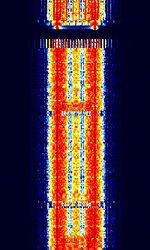 |
|
| FM Broadcast Radio | Commercial Broadcast FMFrequency Modulation radio stations. Used for the broadcast of many different radio programs, including music, news, sports, weather, and talk shows. | 65 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | WFMWideband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 38 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 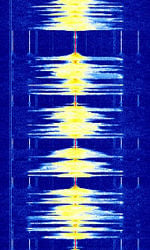 |
|
| Gandalf MDT | Gandalf MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office. was developed by Gandalf Mobile Systems, a subsidiary of Canadian company Gandalf Technologies. Used primarily by taxi and courier services in Canada and the United States. This protocol was used in Gandalf's Cabmate systems. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 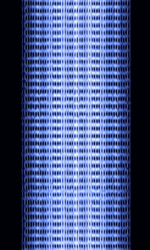 |
|
| Globe Wireless HF Network | Globe Wireless' Maritime Digital Radio was a system of 24 stations around the globe offering data services to large cargo vessels. Since 2014, GW has discontinued their HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) network. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Golay Paging (GSC) | Golay Paging (or Golay Sequential Code, GSC) is a one-way 2-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying paging format developed by Motorola. It is capable of transmitting tone, numeric, alphanumeric, and voice pages. | 33 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 932 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 2.6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 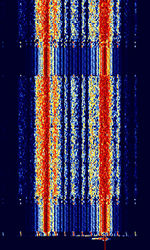 |
|
| Gonets | Gonets (Russian Гонец, for Messenger) is a Russian civilian low Earth orbit communications satellite system. | 265 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 388 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 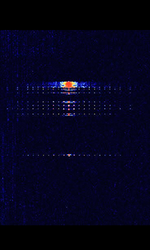 |
|
| HD Radio (AM) | HD Radio is a proprietary digital broadcast radio format transmitted in North America, usually as sidebands on analog carriers. This is the AMAmplitude Modulation band implementation of HD Radio. | 535 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 1.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 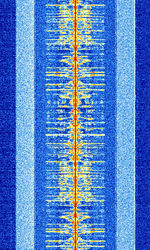 |
|
| HD Radio (FM) | HD Radio is a proprietary digital broadcast radio format transmitted in North America, usually as sidebands on analog carriers. This is the FMFrequency Modulation band implementation of HD Radio. | 87.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 107.9 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 400 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 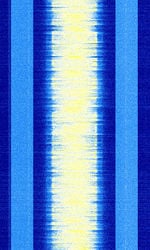 |
|
| HF trading link '120 Hz FMCW idle tone' | A HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) trading link in idle state which strongly resembles an FMCW radar with 120 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). sweep rate. Has been observed to transmit CWContinuous Wave ID once per hour. | 19.31 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20.548 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Canada / Worldwide | 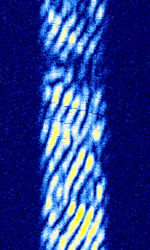 |
|
| Hoffman Broadfield Signpost AVM System | Proprietary FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying data network used for public transport telemetry. It is primarily used to track and control vehicles, and facilitates PTTPush To TalkPress to TransmitMinistries of Postal, Telephone, and Telegraph Service (Soviet Agency)-ID for communication with tram drivers. | 507.225 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 517.875 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 7.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Australia | 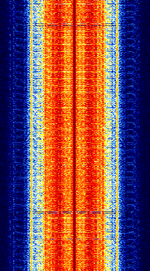 |
|
| IS-54 D-AMPS | D-AMPS, also known as IS-54 and IS-136, is a second generation (2G) mobile phone system standard which develops on analog AMPS, a 1G standard. This system is also colloquially known as TDMATime Division Multiple Access. | 824 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 894 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 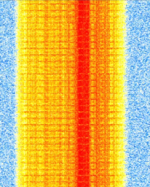 |
||
| Inmarsat Aero | Inmarsat Aero is the protocol that's used to link ground stations with aircraft via Inmarsat's satellite link. This protocol carries digital voice, fax and low speed data such as ACARS and ADS-C. | 1,545 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 3,687 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 800 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 10.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 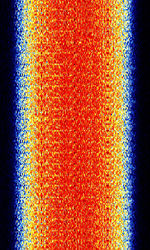 |
|
| Inmarsat IsatM2M | IsatM2M Service operated by Inmarsat on existing Inmarsat-D/D+ infrastructure. | 1,525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,559 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 1.024 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 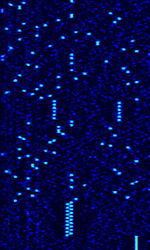 |
|
| Inmarsat-D(D+) Downlink | Inmarsat D+ (and it's predecessor, Inmarsat D) was Inmarsat's satellite paging system. The main use of the technology was in tracking trucks and buoys and SCADA applications. | 1,525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,559 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | MFSKMultiple Frequency Shift-Keying | 640 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide |  |
|
| Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting—Terrestrial (ISDB-T) | ISDB-T (Integrated Services Digital Broadcasting – Terrestrial) is a new type of digital broadcasting system for providing audio, video and multimedia services. ISDB-T system was standardized at the Association of Radio Industries and Businesses (ARIB) in Japan. ISDB-T uses a modulation method referred to as Band Segmented Transmission (BST) OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing. | 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 770 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol), 64QAM | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Japan, Philippines, Argentina, Ecuador, Brazil | — |  |
| Iridium | This is the L-band uplink/downlink for the Low Earth Orbit Iridium Satellite Constellation. This system is used for satellite based phone calls. | 1,616 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,626.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 31.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 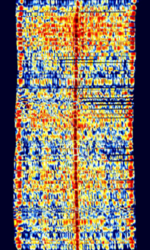 |
|
| IsatData Pro | Inmarsat's M2M data service for SCADA asset tracking and reporting. | 1,525 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,559 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | OQPSK | Worldwide | — |  |
||
| LTE420 MCX | Band 88 FDD | 423.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | 16-QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing | 1.08 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Poland | 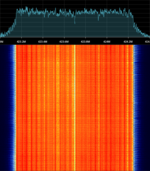 |
|
| LoRa | LoRa (Long Range) is a proprietary low-power wide-area network modulation technique. | 433 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 915 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | CSS | 250 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 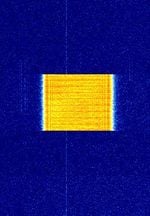 |
|
| Logic Trunked Radio (LTR) | Logic Trunked Radio, is an analog trunked radio format developed by EF Johnson Company. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 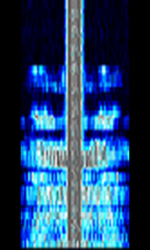 |
||
| MDC1200 | MDC (Motorola Data Communications), also known as Stat-Alert, MDC-1200 and MDC-600, is a Motorola two-way radio low-speed data system. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 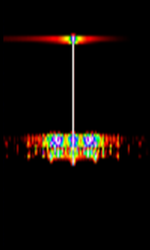 |
|
| MMP-4800 | MMP-4800 was a MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office. (Mobile Data Terminal) protocol developed by Canadian company Mobile Data International (MDI) in 1982 for their Mobile Data Terminals. Used by public safety and commercial industries. Phased out. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 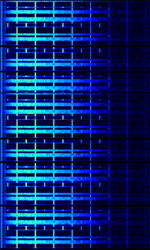 |
||
| MOBITEX | MOBITEX is an OSI based open standard, national public access wireless packet-switched data network. | 400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying, FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 15 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 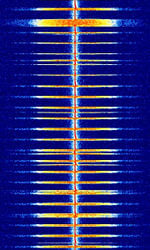 |
|
| Motorola SECURENET | Motorola SECURENET ("analog" encryption) was a secure voice option for conventional and Motorola Type II trunked systems, encoding the voice using 12kbps CVSD and encrypting the bitstream. It is easily identified by the 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz tone at the end of transmission. As it is not 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz FCC narrowbanding mandate compliant, it does not see much use anymore. | 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 16 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 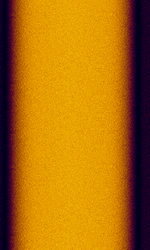 |
|
| Multiple sub-Nyquist Sampling Encoding (MUSE) | Multiplite sub-Nyquist Sampling Encoding (MUSE) also known as Hi-Vision was a early analogue high-defition television standard developed by NHK Science and Technical Research Laboratories. Replaced by digital ISDB broadcast since 2007. | 8,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 12,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | FMFrequency Modulation, DPCM, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation | 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 27 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| Multiplexed Analogue Components (MAC) | Multiplexed Analogue Components (MAC/packet) family was a analogue television broadcasting standard. Replaced by digital broadcast. | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 18,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation, AMAmplitude Modulation, 2PSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol), 4PSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 7.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 22 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| Multitone Paging | Multitone Paging signal, developed by Multitone Electronics in the UK. Uses similar coding to POCSAG but the headers are different and only work with Multitone's range of paging products | 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 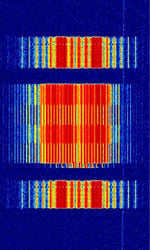 |
|
| NB-IOT | Narrowband Internet of Things (NB-IoTInternet of Things) is a Low Power Wide Area Network (LPWAN) radio technology standard developed by 3GPP to enable a wide range of cellular devices and services. | 700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol) | 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| NTSC Broadcast | National Television System Committee (NTSC) Television broadcast is an analogue television broadcast mode. Currently being phased out in parts of the world in favor of digital broadcast. | 54 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 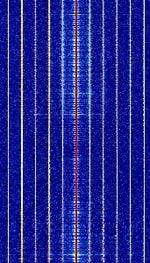 |
|
| Near Field Communication (NFC) | Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (11⁄2 in) or less. | 13.56 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying | 1.7 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 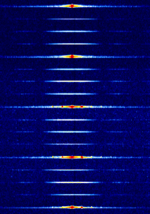 |
||
| Near Instantaneous Companded Audio Multiplex (NICAM) | NICAM is used to provide digital stereo audio alongside PAL video for television broadcasts. | 174 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 400 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
| PACTOR I | PACTOR-I is a digital data protocol combining elements of PACKET and AMTOR ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 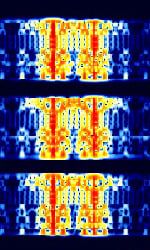 |
|
| PACTOR II | PACTOR II is an advancement of PACTOR I. It is up to 8 times faster than PACTOR I. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 450 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | Worldwide | 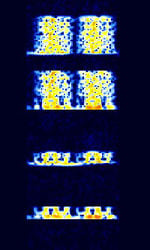 |
|
| PACTOR III | PACTOR III introduces 6 speed levels that provide higher throughput and improved robustness compared to PACTOR I and II. PACTOR III is on average 3.5 times faster than PACTOR II. With optimal conditions, PACTOR III becomes over 5 times faster. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 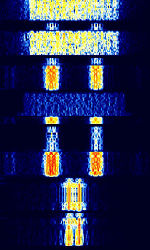 |
|
| PACTOR IV | PACTOR IV is the newest iteration of the PACTOR series, advancing from PACTOR I-III. It is 1.5x-3x faster than PACTOR III, and has 10 speed levels. | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 300 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). — 2.4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 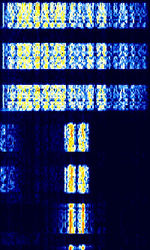 |
|
| PAL Broadcast | Phase Alternating Line (PAL) Analogue Television Broadcast. Now phased out in most of the world. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 862 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 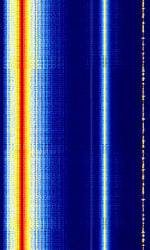 |
|
| POCSAG | POCSAG (Post Office Code Standardisation Advisory Group), also known as Super-POCSAG, Radio Paging Code No. 1 or RPC1, is a one-way 2FSK paging protocol that supports 512, 1200, and 2400 bpsBits per second (bps). | 25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 932 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 9 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 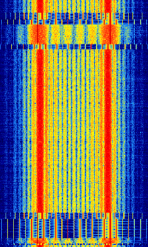 |
|
| Primary Aeronautical Surveillance Radar | A Primary radar (PSR Primary Surveillance Radar) is a conventional radar sensor that illuminates a large portion of space with an electromagnetic wave and receives back the reflected waves from targets within that space. | 1,215 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | Pulse | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 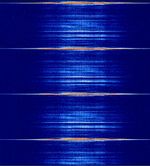 |
|
| Primex Wireless Time Sync | Primex Wireless Time Sync is a VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) Time Synchronization signal used in Primex Wireless's XR Series. | 72.02 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 72.98 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 20 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 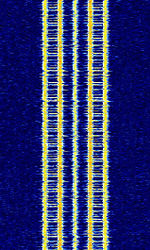 |
|
| RFID | Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. The tags contain electronically-stored information. Passive tags collect energy from a nearby RFID reader's interrogating radio waves. | 125 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 13.56 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, OOKOn-Off Keying Modulation | 3.3 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 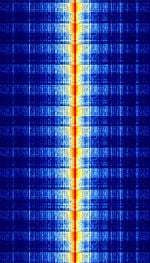 |
|
| Radio Data System (RDS) | Radio Data System (RDS) and its North American variant, Radio Broadcast Data System (RBDS), are data modes transmitted on subcarriers of commercial FMFrequency Modulation radio station transmissions. | 65 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 108 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | DSBDual Side Band Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 4 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 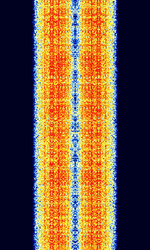 |
|
| Radio-relay link | A radio‑relay (microwave) link using small parabolic antennas is a short‑range, high‑capacity point‑to‑point microwave connection commonly deployed when fiber is unavailable or too expensive to build. | 6,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 38,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying to 2048QAM | 3.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| ReFLEX | ReFLEX is a two-way paging variant of FLEX. | 896 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 40 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 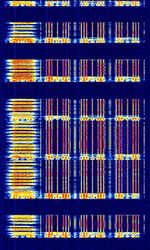 |
|
| S-Band Jammer | This is what the signal of a military S-Band (In this case 2.4 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz) RADAR and WiFi intentional interference (Jamming) device looks like. This signal is generated by a DDS system and is then used to modulate the output of a 2.45 GHzGigaHertz (GHz) 10^9 Hz magnetron (The same as in a microwave oven). | 2,400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Noise | 100 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 100 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — |  |
|
| SECAM | Sequential Colour with Memory (SECAM) Analogue Television Broadcast. Now phased out in most of the world. | 47 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 862 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | VSBVestigial Sideband Modulation, FMFrequency Modulation | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 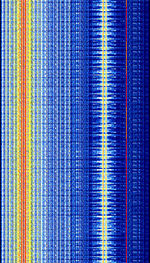 |
|
| SIGFOX | SIGFOX is a IoTInternet of Things wireless network system utilizing ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards.'s specification for Low Throughput Networks (LTN) and Ultra Narrow-Band (UNB) modulation. | 868 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 868.6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | BPSKBinary Phase-Shift Keying (1 bit per symbol) | 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 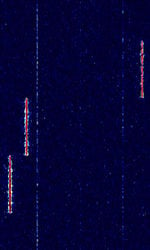 |
|
| STP403 Bus PIT System | STP403 is a bus PITPassenger Information Terminals, such as bus timetable displays at bus stops system used to update digital displays at bus stops. STP403 was developed by French companies INEO and CESATEC. | 164 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 468.488 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 8 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | France | 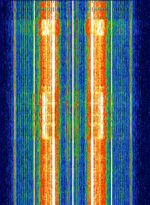 |
|
| Secondary surveillance radar (SSR) | Secondary surveillance radar (SSR)is a radar system used in air traffic control. A surveillance radar system which uses transmitters/receivers (interrogators) and transponders. | 1,030 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | PPMPulse Position Modulation | 3 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 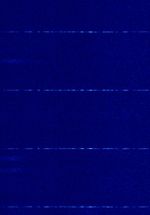 |
|
| Sensus Water meter (Acquisition units) | These are samples from the Sensus Water meters. They are a FHSS ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying encoded data transmission for purposes of providing municipalities water meter telemetry (for billing how much water you use). | 902 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 927 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying, FHSS | 175 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | — | 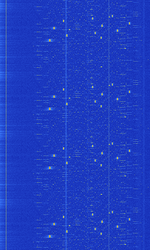 |
|
| SiriusXM Satellite Radio | SiriusXM Satellite Radio: Terrestrial Repeater Signal | 2,332.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 2,345 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 12.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | United States | 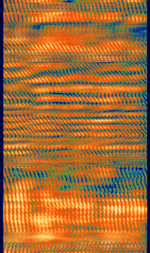 |
|
| TV Satellite Telemetry | These signals are narrowband technical carriers transmitted by the Thor‑5 satellite in the Ku‑band, close to 11700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz. They are part of the satellite’s TT&C (Telemetry, Tracking and Command) and beacon system. | 11,700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 11,702 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | CWContinuous Wave, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 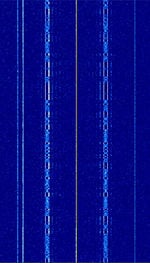 |
||
| Total Access Communication System (TACS) | A first generation analogue mobile cellular system which operated in the United Kingdom and a handful of other countries in Europe. It is also the EU's form of AMPS. | 872 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 960 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation, FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 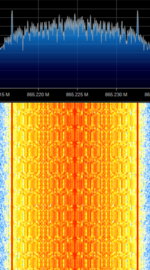 |
|
| UHF Vehicle Location System | UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) Vehicle Location System | 400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 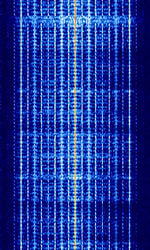 |
|
| UK AM Data System (UK-AMDS) | UK AMAmplitude Modulation Data System (UK-AMDS) was developed by BBC Research and Development in 1984 as a way to transmit low bitrate data on BBC Radio 4's LFLow Frequency (30-300 kHz) AMAmplitude Modulation carrier. Elements of this system were adopted into ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards.'s AMSS. | 198 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | SSBSingle-sideband modulation | AMAmplitude Modulation, PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 85 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | United Kingdom | 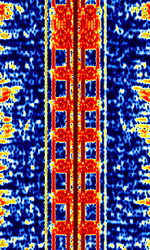 |
|
| Ultra Low Latency (ULL) Electronic Trading Network | A 48k or 24k baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. OQPSK signal that is strongly suspected (through numerous circumstantial pieces of evidence) to be either an experimental or active P2P RFRadio Frequency link between financial market data centers, used for High Frequency Trading (HFT) and other latency-sensitive market activities. | 6 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | OQPSK | 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 60 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 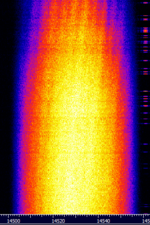 |
|
| Vehicle Counting System | Data transmitted from a vehicle counting system installed in car parks. The data is frequency hopping over 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz. | 915 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 925 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Australia | — |  |
| WiMAX | WiMAX is a family of of wireless broadband communication standards based on the IEEE 802.16 set of standards, which provide physical layer (PHY) and media access control (MAC) options. | OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing, OFDMA | 1.25 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 20 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|||
| Wireless Temperature Sensor | The freezer temperature is requested by a master at regular intervals, and the slave attached to a freezer responds. The communication format appears to be a variant of chirp spread spectrum, (although the spectrum it consumes is quite narrow at ~150 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz). | 434 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | CSS | 150 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Australia | 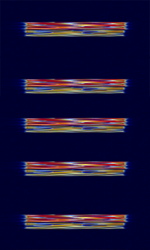 |
|
| Zigbee | Zigbee is a low-power, low-data-rate, low-latency mesh network, based on the IEEE 802.15.4 LR-WPAN standard. It is commonly used for automation and IoTInternet of Things devices, including sensors, light switches/bulbs, and other wireless-controlled devices. | 868 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 2,480 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | AMAmplitude Modulation | QQPSK, DSSS | 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | Worldwide | 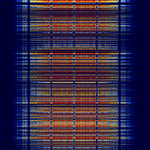 |
Pages in category "Commercial"
The following 106 pages are in this category, out of 106 total.