Near Field Communication (NFC)
 | |
|---|---|
| Frequencies | 13.56 MHz |
| Frequency Range | 13.56 MHz - 13.56 MHz |
| Mode | — |
| Modulation | ASK |
| ACF | — |
| Emission Designator | — |
| Bandwidth | 1.7 MHz |
| Location | Worldwide |
| Short Description | Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (11⁄2 in) or less. |
| I/Q Raw Recording | Download file |
| Audio Sample | |
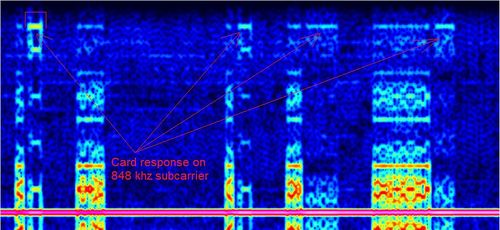
Near-field communication (NFC) is a set of communication protocols that enables communication between two electronic devices over a distance of 4 cm (11⁄2 in) or less. Like other "proximity card" technologies, NFC is based on inductive coupling between two so-called antennas present on NFC-enabled devices—for example a smartphone and a printer—communicating in one or both directions, using a frequency of 13.56 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz in the globally available unlicensed radio frequency ISM band using the ISO/IEC 18000-3 air interface standard at data rates ranging from 106 to 424 kbit/sKilobits per second (kbps).
Reception note: The signal is very weak when received on a whip antenna at close range, leaving only a narrow part of it on the waterfall (like ADS-B). I used a coil of wire 40 meters long for reception of full signal(and 2-4 Msps samplerate) .