4G LTE Network
| Cellular | |
|---|---|
| 1G: AMPS - NMT 2G: GSM - D-AMPS - 2G CDMA (IS-95) |
 | |
|---|---|
| Frequencies | 3500 MHz,450 MHz,600 MHz,700 MHz,800 MHz,900 MHz,1800 MHz,2100 MHz,2300 MHz,2600 MHz |
| Frequency Range | 450 MHz - 3500 MHz |
| Mode | OFDM |
| Modulation | QPSK,16QAM,64QAM,256QAM |
| ACF | — |
| Emission Designator | — |
| Bandwidth | 20 MHz,1.4 MHz,3 MHz,5 MHz,10 MHz,15 MHz |
| Location | Worldwide |
| Short Description | Long Term Evolution Network. Also known as 4G LTE Data and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA). Data service for wireless consumer devices. |
| I/Q Raw Recording | Download file |
| Audio Sample | |
Long Term Evolution Network. Also known as 4G LTE Data and Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA). Data service for wireless consumer devices.
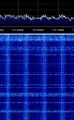
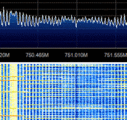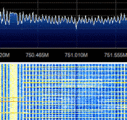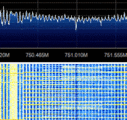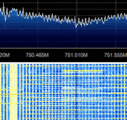
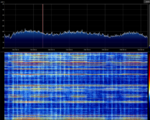
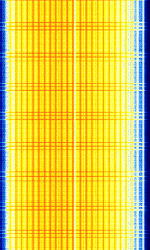
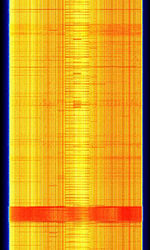
LTE uses OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing) modulation. In a LTE channel, it is divided into resource blocks. Each resource block is 180kHz in bandwidth. In each of the resource blocks, there are many subcarrier channels which are spaced 15kHz away from each other. The DC subcarrier (blank) is present in the middle to mitigate the effect of LO leakage.
For a 20MHz channel, there could be up to 1024 subcarriers. The high number of subcarriers will allow for more users to use the network simultaneously. Carrier Aggregation (used in LTE-Advanced) increases the bandwidth further. LTE can be either FDD (Frequency Division Duplex) and TDD (Time Division Duplex) depending on the network configuration.
Modulation[edit]
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing: Quadrature Phase Shift Keying (OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing-QPSKQuadrature Phase-Shift Keying (2 bits per symbol))
- Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing: Quadrature Amplitude Modulation (OFDMOrthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing-QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation)
Frequencies[edit]
List of frequencies can be found here.
Decoding Software[edit]
- Hobby Level Software
Video Examples[edit]
Additional Links[edit]
- More information on LTE
- Wikipedia E-UTRA
- Switzerland Federal Office of Communications: LTE Factsheet
- 3GPP Information on LTE
- LTE; Evolved Universal Terrestrial Radio Access (E-UTRA) Physical Channels and Modulation, ETSI report
Additional Images[edit]
Sound Samples[edit]
| 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz Orange | 10 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz T-Com | 1.4 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz Vodafone |
|---|---|---|
| IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis.: File:LTE OR 10 downlink.zip | IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis.: File:LTE TK 10 downlink.zip | IQQuadrature signals form the basis of complex RF signal modulation and demodulation, both in hardware and in software, as well as in complex signal analysis.: File:LTE VF 1.4 downlink.zip |
FDD Mode[edit]
TDD Mode[edit]