Land-Mobile Radio
From Signal Identification Wiki
Land-mobile radio covers one-to-many communications with mobile or portable users, possibly through a mobile relay or trunking system. Such systems are almost always found on VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) and UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz), although a handful of HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) systems are in use for long-haul mobile communications. Compare to fixed links, where all stations are immobile.
Click the name of a signal to see more detailed information, possible decoding, and additional sound and waterfall samples
| Inactive (No longer in use) |
Active (Currently in active use) |
Status Unknown or Intermittent |
| Signal Name | Description | Frequency | Mode | Modulation | Bandwidth | Location | Sample Audio | Waterfall image |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Autocab | This is an example of the Autocab Media Data Terminals used by cab companies all over the world. | 163.375 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United Kingdom | 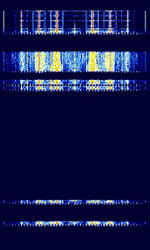 |
|
| Automatic Identification System (AIS) | Automatic Identification System (AIS) is used by ships to broadcast position and vessel information. | 161.975 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 162.025 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 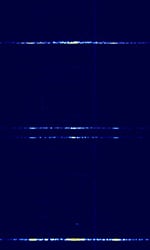 |
|
| Continuous Tone-Coded Squelch System (CTCSS) | CTCSS, also known as Private Line and Channel Guard, is a low continuous tone transmitted on NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation voice transmissions that is used to squelch and manage transmissions on a given frequency. | 30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | CWContinuous Wave | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 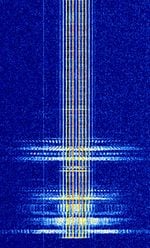 |
|
| D-STAR | D-STAR is a digital voice protocol used by ham radio. Is sometimes routed over the internet for international communications. | 145.67 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 6.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 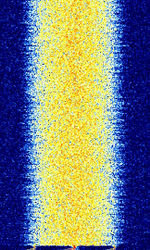 |
|
| Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) | Digital Mobile Radio (DMR) is an open digital mobile radio standard defined by ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards. and used in commercial products around the world. Mostly used by private network and local police, can be encrypted. Used in MOTOTRBO products. | 66 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 860 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 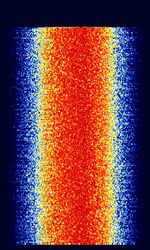 |
|
| Digital Private Mobile Radio (dPMR) | dPMR is an open, non-proprietary trunked radio standard developed by ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards., published under ETSIEuropean Telecommunications Standards Institute. An independent, not-for-profit, standardization organization in the telecommunications industry in Europe, developing global telecommunications standards. TS 102 658. Supports both data and digital voice transmission. | 149.019 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 446.2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 6.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 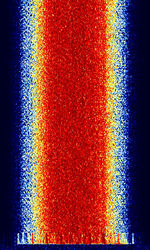 |
|
| Enhanced Digital Access Communications System (EDACS) | EDACS is a trunked radio system developed by General Electric and Ericsson. EDACS was invented by General Electric in the mid-80s and is currently owned by Harris Corporation. Harris has announced that EDACS systems will no longer be supported by 2017. | 160 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 6.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 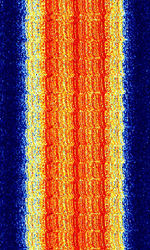 |
|
| Gandalf MDT | Gandalf MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office. was developed by Gandalf Mobile Systems, a subsidiary of Canadian company Gandalf Technologies. Used primarily by taxi and courier services in Canada and the United States. This protocol was used in Gandalf's Cabmate systems. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 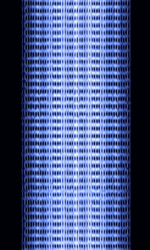 |
|
| Integrated Digital Enhanced Network (iDEN) | iDEN is a TDMATime Division Multiple Access-based digital wireless standard developed by Motorola. It is a type of trunked radio with cellular phone benefits. | 806 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 869 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation, TDMATime Division Multiple Access | 18.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 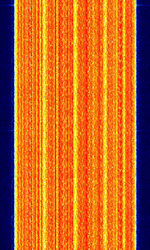 |
|
| LoJack | LoJack is a vehicle tracking system that allows vehicles to be tracked by police, with the aim of recovering them in case of theft via a small radio transceiver clandestinely installed in a vehicle. | 173.075 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| Logic Trunked Radio (LTR) | Logic Trunked Radio, is an analog trunked radio format developed by EF Johnson Company. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 470 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | 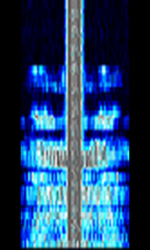 |
||
| MDC-4800 | Motorola's MDC-4800 is a data protocol that was used in ARDIS and DataTAC Networks as well as in MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office. networks. RD-LAP was derived from this mode. Also known as Motorola Mobile Data Communications System (MODACOM) | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 850 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide |  |
|
| MPT 1327 | MPT1327 (Ministry of Posts and Telegraph 1327) is a signaling protocol standard for analog trunked radio | 162.5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying, FMFrequency Modulation | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 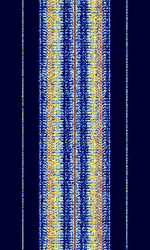 |
|
| Motorola ASTRO 25 HPD Air Interface | Motorola's ASTRO 25 High Performance Data Air Interface allows Motorola ASTRO 25 HPD modems to transfer data at up to 96 kbpsKilobits per second (kbps) over a 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz channel in the 700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz or 800 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz bands. | 769 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 869 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | QAMQuadrature Amplitude Modulation | 17.7 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 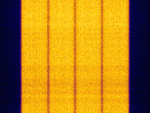 |
|
| Motorola SECURENET | Motorola SECURENET ("analog" encryption) was a secure voice option for conventional and Motorola Type II trunked systems, encoding the voice using 12kbps CVSD and encrypting the bitstream. It is easily identified by the 6 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz tone at the end of transmission. As it is not 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz FCC narrowbanding mandate compliant, it does not see much use anymore. | 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 16 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 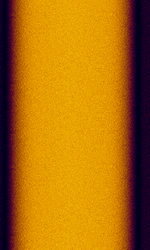 |
|
| Motorola Type II | Radio trunking control channel. | 136 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 16 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 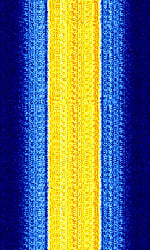 |
|
| NFM Voice | Used in analog walkie-talkies and communication systems. | 27 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 864 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 30 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 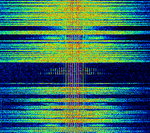 |
|
| Next Generation Digital Narrowband (NXDN) | NXDN is a digital narrowband trunked radio protocol used in commercial, business & industry, transport and Public Safety professional radio systems. | 136 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 520 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 6.25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 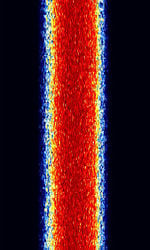 |
|
| OpenSky | OpenSky is an encrypted TDMATime Division Multiple Access protocol that is heavily used but is being phased out by the Pennsylvania State Police. No one other than the intended user has been able to decrypt the signal. | 700 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 1,000 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | TDMATime Division Multiple Access, 4GFSK | 20.07 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 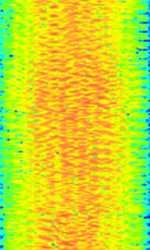 |
|
| ProVoice | ProVoice is a digital voice mode used in EDACS trunked systems. | 160 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GFSKGaussian Frequency-Shift Keying | Worldwide | 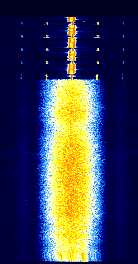 |
||
| Project 25 (P25) | Project 25 (P25 or APCO-25) is a trunked radio standard developed by The Association of Public Safety Communications Officials International (APCO-25) for use with public safety organizations around the world. | 136 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 939 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying, C4FMContinuous 4-Level Frequency Modulation, TDMATime Division Multiple Access | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 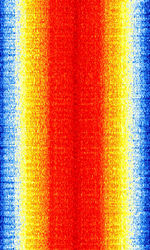 |
|
| Radio Data Link Access Procedure (RD-LAP) | Motorola's Radio Data Link Access Procedure (RD-LAP) is a 1G protocol that was used in ARDIS and DataTAC Networks, and is still used in some MDTMobile Data Terminal, A mobile data terminal (MDT) is a computerized device used in public transit vehicles, taxicabs, commercial trucking fleets, military logistics, and emergency vehicles, such as police cars, to communicate with a central dispatch office.'s, as well as gas companies, police departments, fire departments, financial companies, etc. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 850 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | 4FSK4-Level Frequency Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 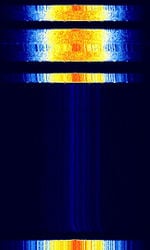 |
|
| ReFLEX | ReFLEX is a two-way paging variant of FLEX. | 896 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 941 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FFSKFast Frequency-Shift Keying | 40 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 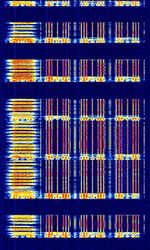 |
|
| Terrestrial Trunked Radio (TETRA) | TETRA is a professional mobile radio and two-way transceiver (walkie-talkie) specification | 380 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 860 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 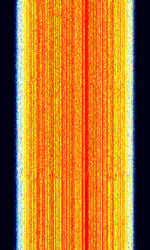 |
|
| Tetrapol | Tetrapol is a digital professional mobile radio standard for digital voice and data communication used by public safety and military throughout Europe. Tetrapol was originally developed by Matra Communication (Currently part of EADS/Airbus Group) in France in the 1980's. | 370 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | GMSKGaussian Minimum-Shift Keying | 10 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz — 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Europe | 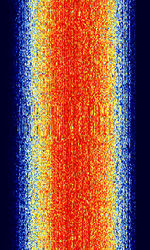 |
|
| UHF Vehicle Location System | UHFUltra High Frequency (300-3000 MHz) Vehicle Location System | 400 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 900 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FSKFrequency-Shift Keying | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | United States | 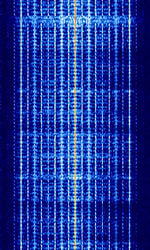 |
|
| VHF Data Link - Mode 2 (VDL-M2) | VDL-M2 (Known as VDL2 or VDLM2) is a means of sending information between aircraft and ground stations. VDL Mode 2 is the only VDL mode being implemented operationally to support Controller Pilot Data Link Communications (CPDLC). An extension to the AVLC protocol permits ACARS over AVLC (AOA) transmissions. VDL-M2 is implemented by Eurocontrol. | 117.975 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 137 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | RAW | PSKPhase-Shift Keying | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 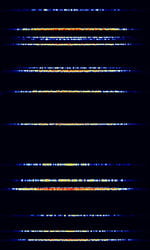 |
|
| Voice Inversion Scrambling | Analog Voice Inversion Scrambling divides the spectra into multiple bands and swaps them. | 150 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | NFMNarrowband Frequency Modulation | FMFrequency Modulation | 25 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 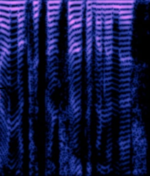 |
|
| Yaesu System Fusion | System Fusion is Yaesu's digital voice/data protocol for amateur radio, using the AMBE+2 vocoder on a C4FMContinuous 4-Level Frequency Modulation signal. | 144 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz — 450 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz | FMFrequency Modulation | C4FMContinuous 4-Level Frequency Modulation | 12.5 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz | Worldwide | 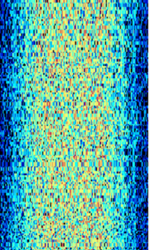 |
Pages in category "Land-Mobile Radio"
The following 29 pages are in this category, out of 29 total.
ACDEGIL |
L cont.MNOP |
P cont.RTUVY |