TWINPLEX
TWINPLEX, also known as F7B4 and TWINPLEX-SITOR, was a diplex 4-FSKFrequency-Shift Keying ARQAutomatic Repeat reQuestAutomatic Repeat Query mode developed by Mackay Radio and Telegraph Company, based in New York City, in the early 1950s. This mode was used by Interpol, the United Nations, and many government diplomatic services all over the world, including Australia, Denmark, The Netherlands, Norway, Pakistan and Spain.
TWINPLEX was developed to try to double the throughput of a single telegraph channel while still staying within a single channel's bandwidth. Two separate channels can be transmitted simultaneously using TWINPLEX; the two channels can even be at different data rates.'
Characteristics[edit]
TWINPLEX employs two channels that are transmitted via the 4 FSKFrequency-Shift Keying methods. Each frequency used represents two symbols, each symbol representing either a mark or space for each of the two channels transmitted. TWINPLEX typically runs at 100 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second., but rarely at 200 or 300 bdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second..
The bandwidth of TWINPLEX varies, from 450 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). to 950 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). depending on setup.
This is an example of a TWINPLEX signal with a setup of 115-170-115: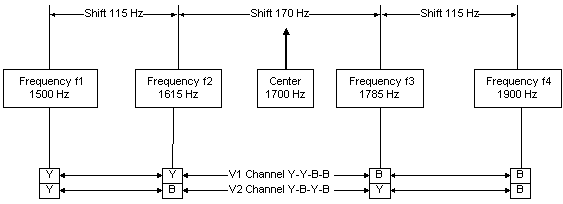
Each TWINPLEX transmission can be determined by the three shifts between the 4 frequencies used in the A-B-C format.
TWINPLEX stations only key the two inner frequencies, f2 and f3, during the IDLE state (no traffic) or during the RQ state. In these states, SITOR and TWINPLEX systems cannot be distinguished from each other.
Variants[edit]
The Mackay Radio and Telegraph Company also developed two derivative modes from TWINPLEX, dubbed TWINMODE and POLYPLEX.
TWINMODE[edit]
TWINMODE is the transmission of two TWINPLEX signals simultaneously. This allows for 4 simultaneous channels to be transmitted. The original TWINPLEX channels are transmitted as usual, but the additional two channels are AMAmplitude Modulation Modulated in subcarriers flanking the original TWINPLEX signal at a frequency shift that allows ordinary TWINPLEX receivers to be able to decode, maintaining compatibility.
POLYPLEX[edit]
POLYPLEX is a further jump from TWINPLEX where up to 8 simultaneous channels are supported. It employs Twinplex equipment as basic building blocks, adding units for shifting a subcarrier at approximately 200 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz by each Twinplex Combiner, mixing these together with a 1.8 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz frequency, selecting the upper side bands centered at 2 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz, selecting the lower side bands centered at the operating frequency and amplifying it in SSBSingle-sideband modulation operation. Receivers are standard TWINPLEX receivers with their tuning adjusted to the offset of the desired pair of channels within the 1600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). - 3400 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). pass band of their input filter. In this way, each telegraph channel has complete independence from all other channels.
Setups for TWINPLEX[edit]
The standard setups for TWINPLEX are:
- 100-100-100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).
- 200-400-200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).
- 170-170-170 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).
- 115-170-115 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).
- 200-200-200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).
- 115-170-515 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). (Asymmetrical)
- 65-170-65 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).
Samples[edit]
| 200-400-200 Denmark Diplomatic |
115-170-115 Spain Diplomatic |
115-170-515 Pakistani Diplomatic |
|---|---|---|
Additional Samples[edit]
Asymmetrical (all 100 BdBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.):Decoding Software[edit]
- Professional Equipment/Software
- go2DECODE
- go2MONITOR
- Hoka Code 300-32
- Wavecom W-Code
- Wavecom W-Spectra
- Rohde&Schwarz CA100
Additional Links[edit]
- RadioReference.com TWINPLEX
- Digital Signals
- TWINPLEX: Electrical Communication, March 1952
- shoc Database: TWINPLEX
- WAVECOM Database: TWINPLEX
- IEEE Twinplex, Twinmode, and Polyplex Radiotelegraph Systems



