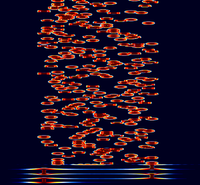
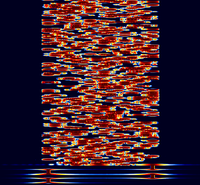
RTTYM
OLIVIA based Modes: Olivia - Contestia - RTTYM - PAX - VOICE
RTTYM, developed by Nick Fedoseev (UT2UZ) in 2005, is a digital mode derived from Olivia. It aims to deliver a compromise of speed and performance. RTTYM is about 4x faster than Olivia, but trades the speed for reduced robustness and sensitivity.
Compared to Olivia, RTTYM has +3 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal. minimum signal to noise ratio compared to Olivia. RTTYM uses a block size of 16 where Olivia uses a block size of 64. RTTYM uses a slightly modified RTTY Baudot 5-bit alphabet encoding.
RTTYM Submodes[edit]
125, 250, 500, 1000, and 2000 are the available bandwidths. 4, 8, 16, 32, 64, 128, and 256 are the available tones. There are a total of 40 possible submodes.
RTTYM's submodes are determined by bandwidth and number of tones. This is represented with the "RTTYM X/Y" or "RTTYM X-Y" format, where X = # of tones and Y = Bandwidth in HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).. Y/X is also alternatively used. E.g: RTTYM 8-250 = 8/250 = 250/8 = 8 tones, 250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). bandwidth.
The standard RTTYM submodes (bandwidth/tones) are 4/125, 8/250, 16/500, 32/1000, and 64/2000.
The most commonly used submodes right now are 8/125, 4/250, 8/250, 4/500, 8/500, 16/500, 8/1000, 16/1000 and 32/1000.
| 2/125 | 4/125 | 8/125 | 16/125 | 32/125 | 64/125 | 128/125 | 256/125 |
| 2/250 | 4/250 | 8/250 | 16/250 | 32/250 | 64/250 | 128/250 | 256/250 |
| 2/500 | 4/500 | 8/500 | 16/500 | 32/500 | 64/500 | 128/500 | 256/500 |
| 2/1000 | 4/1000 | 8/1000 | 16/1000 | 32/1000 | 64/1000 | 128/1000 | 256/1000 |
| 2/2000 | 4/2000 | 8/2000 | 16/2000 | 32/2000 | 64/2000 | 128/2000 | 256/2000 |
Mode Characteristics[edit]
- 8-250: "Slow" 8 tones, bandwidth=250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz)., speed=31.25 bauds, 58 wpm, lowest S/N=-12 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal.,
- 16-500: "Average" 16 tones, bandwidth=500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz)., speed=31.25 bauds, 78 wpm, lowest S/N =-10.5 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal.,
- 32-1000: ("Standard" default mode) 32 tones, bandwidth=1000 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz)., speed=31.25 bauds, 97 wpm, lowest S/N =-10 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal.,
- 8-500: "Normal" 8 tones, bandwidth=500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz)., speed=62.5 bauds, 117 wpm, lowest S/N =-9 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal.,
- 16-1000: "Fast" 16 tones, bandwidth=1000 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz)., speed=62.5 bauds, 156 wpm, lowest S/N =-7.5 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal.,
- 4-500: "Fast 2" 4 tones, bandwidth=500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz)., speed=125 bauds, 156 wpm, lowest S/N =- 6 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal..
- 4-250: "Average 2" 4 tones, bandwidth=250 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz)., speed=62,5 bauds, 78 wpm, lowest S/N =-8.5 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal.,
- 8-1000: "Very fast" 8 tones, bandwidth=1000 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz)., speed=125 bauds, 234 wpm, lowest S/N =-3 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal..
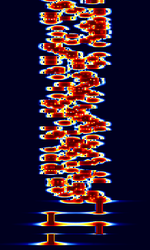
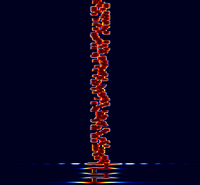
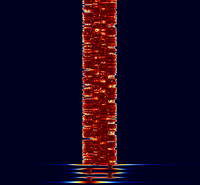
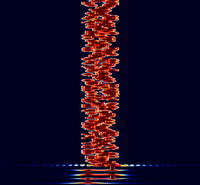
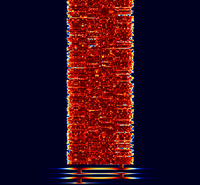
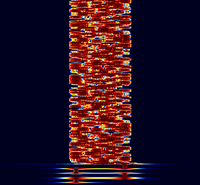
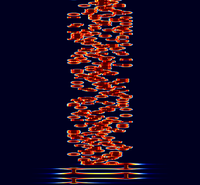
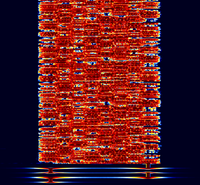
Samples[edit]
| 8/125 | 4/250 | 8/250 |
|---|---|---|
| 4/500 | 8/500 | 16/500 |
|---|---|---|
| 8/1000 | 16/1000 | 32/1000 |
|---|---|---|
Frequencies[edit]
Decoding Software[edit]
- Hobby Level Software
Additional Links[edit]
- AC4M Digital Modes Contestia and RTTYM
- A Field Guide to the DM-780 Digimode Traces
- MULTIPSK Contestia and RTTYM