MPDA
MPDA (short for Multi-Parallel Differential Amplitude Shift Keying) is a robust, narrowband digital communication protocol designed for amateur radio text transmission over HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) and VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) bands. Developed by amateur radio operator 6L5TNG (Kang Han) from the Republic of Korea, this protocol specifically utilizes an Intra-Symbol Differential modulation scheme to achieve spectral efficiency and exceptional robustness against fading (QSB).
Technical Overview[edit]
| Parameter | Specification |
|---|---|
| Full Name | Multi-Parallel Differential Amplitude Shift Keying |
| Type | Digital Data (Text) |
| Frequency Range | HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) (1.8–30 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz), VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) |
| Location | Worldwide (Developed in Republic of Korea) |
| Audio Range | 600 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). – 2200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). (depending on mode) |
| Bandwidth | ~2000 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). |
| Sample Rate | 44100 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). |
Signal Structure[edit]
The MPDA signal employs a unique Intra-Symbol Differential structure to resist fading:
- Pilot Tone: A 2200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). tone precedes the data burst to wake up the receiver and establish AGC/timing lock.
- Gap: A fixed silence period (0.15s) separates the pilot and the data burst.
- Preamble: Three bytes of
0xAAare sent for bit synchronization. - Payload (Differential Encoding): Each symbol period is split into two halves:
- First Half (Reference): Fixed amplitude of 0.5. Serves as a local reference for the channel condition.
- Second Half (Data): Carries the bit information.
- Logic 1: High Amplitude (1.0) – Louder than reference.
- Logic 0: Soft-Low Amplitude (0.1) – Quieter than reference.
- The receiver compares the Data half against the Reference half, allowing correct decoding even if the overall signal strength fluctuates (fading).
- Postamble: Three bytes of
0xFFsignal the end of transmission (EOTEnd of Transmission).
MPDA Submodes[edit]
MPDA modes are identified by the notation MPDA-<tracks>x<baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.>.
- Tracks (Parallel Tones): The number of simultaneous audio carriers transmitting data.
- More tracks = Higher throughput (sending more bits at the same time).
- BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. (Symbol Rate): The modulation speed (how many times per second the signal state changes).
- Lower baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. = Higher robustness against multi-path propagation delays.
Note on Speed: The raw bit rate is calculated as Tracks × Symbol Rate. For example, MPDA-4x10 achieves 40 bpsBits per second (bps) (4 tracks × 10 baudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second.).
| Mode Name | Tracks | Symbol Rate | Raw Bit Rate | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MPDA-1x5 | 1 | 5 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 5 bpsBits per second (bps) | Very robust, very slow |
| MPDA-1x10 | 1 | 10 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 10 bpsBits per second (bps) | Robust single-track |
| MPDA-1x15 | 1 | 15 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 15 bpsBits per second (bps) | Faster single-track |
| MPDA-4x5 | 4 | 5 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 20 bpsBits per second (bps) | Robust multi-track |
| MPDA-4x10 | 4 | 10 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 40 bpsBits per second (bps) | Default / Reference Mode |
| MPDA-4x15 | 4 | 15 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 60 bpsBits per second (bps) | Fast multi-track |
| MPDA-8x5 | 8 | 5 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 40 bpsBits per second (bps) | Many tracks, low rate |
| MPDA-8x10 | 8 | 10 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 80 bpsBits per second (bps) | High throughput |
| MPDA-8x15 | 8 | 15 BaudBaud (unit symbol Bd) is the unit for symbol rate or modulation rate in symbols per second. | 120 bpsBits per second (bps) | Maximum speed |
Unless otherwise noted, MPDA-4x10 is considered the reference mode used in most examples.
Mode Characteristics[edit]
- Robust Modulation: Uses AFSKAudio Frequency-Shift Keying-based Multi-tone ASKAmplitude-Shift Keying. Unlike traditional FSKFrequency-Shift Keying, MPDA utilizes amplitude states across multiple parallel carriers.
- Phase Continuity: The transmitter generates Phase-Continuous waveforms to eliminate key clicks and minimize splatter.
- DSP-Based Demodulation: The receiver utilizes Matched Filter Correlation (Coherent Detection), which offers superior performance in low SNR environments.
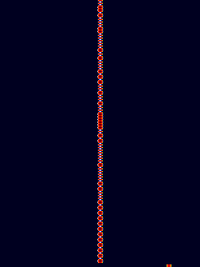
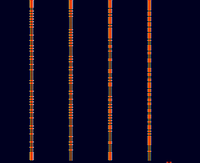
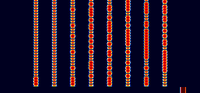
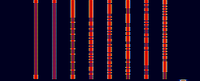
Samples[edit]
| 1×5 | 1×10 | 1×15 |
|---|---|---|
| 4×5 | 4×10 | 4×15 |
|---|---|---|
| 8×5 | 8×10 | 8×15 |
|---|---|---|
Frequencies[edit]
MPDA is designed for use in standard SSBSingle-sideband modulation (USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)) voice channels on HFHigh Frequency (3-30 MHz) and VHFVery High Frequency (30-300 MHz) bands. The specific audio frequencies used within the passband are:
- 1-Track Mode: 1500 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).
- 4-Track Mode: 800, 1200, 1600, 2000 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).
- 8-Track Mode: 600, 800, ..., 2000 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). (200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). spacing)
- Pilot Tone: 2200 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). (Always used for sync)
Decoding Software[edit]
Currently, there is no standalone application available for end-users. Please refer to the project link below for the source code and usage examples.
The official implementation is provided as a Python library:
- Core Logic: Encapsulated in
mpda_core.py. - Transmitter: Generates phase-continuous float32 audio arrays to prevent key clicks.
- Receiver: Uses matched filters (correlation) to detect symbols even in low SNR conditions.