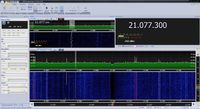
JT65
 | |
|---|---|
| Frequencies | 24.917 MHz,1.838 MHz,3.576 MHz,7.039 MHz,7.076 MHz,10.139 MHz,14.076 MHz,18.102 MHz,18.098 MHz,50.276 MHz |
| Frequency Range | 1.838 MHz - 50.276 MHz |
| Mode | USB |
| Modulation | MFSK |
| ACF | — |
| Emission Designator | — |
| Bandwidth | 180 Hz,360 Hz,710 Hz |
| Location | Worldwide |
| Short Description | JT65 is an amateur radio QSO communication protocol developed by Joe Taylor, K1JT. JT65 has 3 submodes: JT65A, JT65B, and JT65C. The most popular submode of JT65 is JT65A. JT65 gets '65' from the 65 tones it uses. |
| I/Q Raw Recording | — |
| Audio Sample | |
JT65 is an amateur radio QSO communication protocol developed by Joe Taylor, K1JT. JT65 has 3 submodes: JT65A, JT65B, and JT65C. The most popular submode of JT65 is JT65A. JT65 gets '65' from the 65 tones it uses.
Each transmission begins at t = 1s after the start of a UTC minute and finishes at t = 47.8 s. Each transmission must begin within the first 4 seconds of the minute to be decoded. Multiple stations transmit on the same carrier using both FDM and TDM methods. Initiating stations choose either the Even or Odd minute to transmit and responding stations transmit on the opposite minute.
A sync (low) tone is to mark the lower boundary of each station's signal. The synchronizing tone is at 1270.5 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).. The initiating station is responsible for choosing an offset that does not conflict with another station's signal. JT65 uses 126 contiguous time intervals, each of length 0.372 s (4096 samples at 11025 samples per second). Within each interval, the waveform is a constant-amplitude sinusoid at one of 65 pre-defined frequencies, and frequency changes between intervals are accomplished in a phase-continuous manner.
Submodes[edit]
The three main submodes, JT65A, B, and C, differ in the frequency shifts between each of the 65 tones. For JT65A, the shift is 2.7 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).. For JT65B, it's 5.4 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).. For JT65C, it's 10.8 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz).. The general rule used is the resolution function 2.7m, where A uses m=1, B uses m=2, and C uses m=4.
Two experimental submodes, JT65B2 and JT65C2 are twice as fast as their counterpart JT65B and JT65C respectively. The tone frequency shifts are the same.
| Submode | Tone spacing | Bandwidth | Minimum SNR for decoding |
|---|---|---|---|
| JT65A | 2.69 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | 178 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | -25 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal. |
| JT65B | 5.38 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | 353 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | -25 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal. |
| JT65C | 10.8 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | 703 HzHertz (Hz), unit of frequency, defined as one cycle per second (1 Hz). | -25 dBThe decibel (dB) is a logarithmic unit used to express the ratio of two values of a physical quantity, here the strength of a received signal. |
Samples[edit]
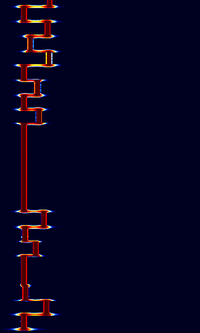
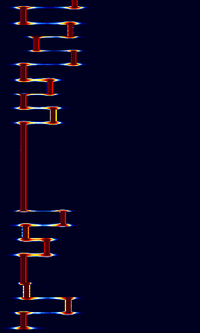
| JT65A | JT65B | JT65C |
|---|---|---|
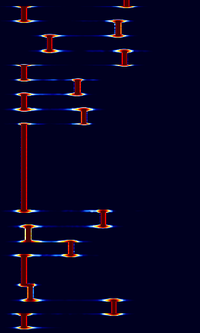
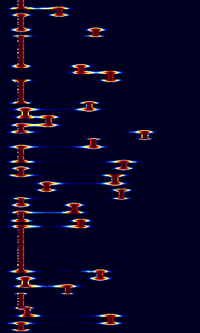
| JT65B2 | JT65C2 |
|---|---|
Frequencies[edit]
The signals are usually found in the data portion of the Amateur Radio Bandplans between the CWContinuous Wave (Morse) and the PSKPhase-Shift Keying/RTTYRadio TeleTYpe windows. They are always transmitted in USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables) mode regardless of band.
The most popular JT65A frequency is in the 20 Meter band.
- 160m: 1838.0 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)
- 80m: 3576.0 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)
- 40m International: 7039.0 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)
- 40m USA: 7076.0 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)
- 30m: 10139.0 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables).
- 20m: 14076.0 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)
- 17m: 18102.0 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables).
- 17m Alternate: 18098.0 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)
- 12m: 24917.0 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)
- 6m EME: 50276 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz USBUpper Side Band Modulation (Radio, referring to reception and modulation mode)Universal Serial Bus (Computer, referring to USB Ports and cables)
JT65B examples -
- 2m UK Beacon: 144,430 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz Kent
- 70cm UK Beacon: 432,430 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz Kent
JT65C example -
- 23cm UK Beacon: 1,296,800 kHzKiloHertz (kHz) 10^3 Hz Isle of Wight
- JT65A Frequencies via HFLink.com
- See the ARRL Frequency Allocations page for the US use of 5 MHzMegaHertz (MHz) 10^6 Hz
Decoding Software[edit]
- Hobby Level Software
- MAP65
- WSJT
- WSJT-X (multi-platform)
- JT65-HF (Windows)
- JT65-HF-Comfort (Windows)
- JT65-HF-HB9HQX-Edition (Windows)
- MultiPSK (Windows)
- MixW4 (Windows)
Video Examples[edit]
Additional Links[edit]
- I-56578 JT65 (Italian)
- JT65A on NW7US's website.
- JT65-HF on IZ4CZL's website
- WSJT on Wikipedia
- JT65 Communications Protocol
- JT65A on HF group on Facebook.com
- GB3VHF / GB3UHF JT65B beacon information (located in SE England)